Metal 3D Printing vs CNC Machining: Competition or Complementarity
More design freedom and flexibility are the driving factors to reduce waste, improve productivity and obtain functional gains. The core advantages of Metal 3D Printing are gradually known to the market. At the same time, repetitive mass production, surface finishing and precision tolerance are still the irreplaceable advantages of CNC processing. This article will discuss why these two manufacturing technologies could and should be regarded as complementary rather than contradictory in many cases.
Learn about how 3D Printing and CNC Machining process metal
How 3D Printing Processes Metal
There are about ten ways to manufacture metal parts with 3D printing on the market. These methods are roughly divided according to the raw material form and energy source used, such as whether the material is a metal wire or metal powder, including metal resin, metal bars and metal particles. Each method can produce parts with different properties.

Selecting which metal technology to use requires considering factors such as part details, shape, size, strength, metal types, cost, printing speed and quantity. If analyzed from these aspects, each technology has its pros and cons. Unfortunately, it’s impossible to print super powerful parts quickly, cheaply and flawlessly, so choosing which technology to use is necessary according to the application requirements.
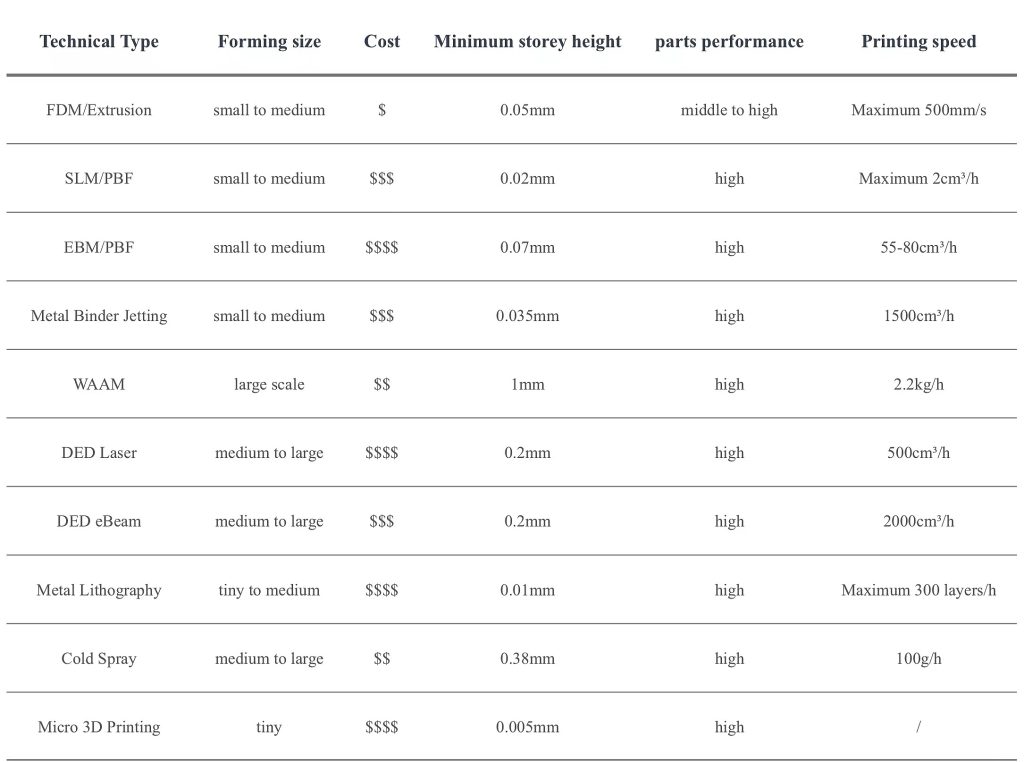
Table 1. 10 Best Ways to Manufacture Metal Parts with 3D Printing
Take the SLM 3D printer as an example; it uses a high-power laser to melt metal powder selectively and accounts for the highest proportion among metal 3D printers. In addition, the printer can use either "pure" metal materials or alloy materials.
SLM 3D printer uses powdery metal materials. After being put into the print bin, the metal powder is spread on the substrate or construction platform by a scraper or roller to form a thin layer. Next, a high-power laser selectively melts the powder material according to the pattern of slices. Then, the construction board drops to the height of a small layer, and the coater spreads another layer of new powder on the surface. The printer repeats these steps until the finished part is available.

How CNC Processes Metal
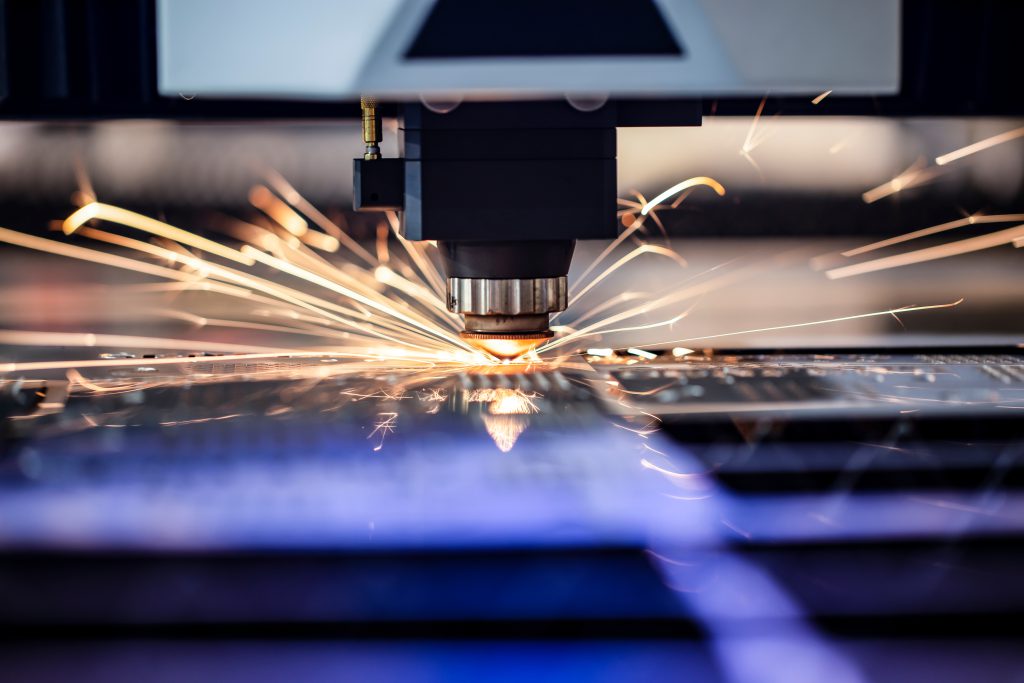

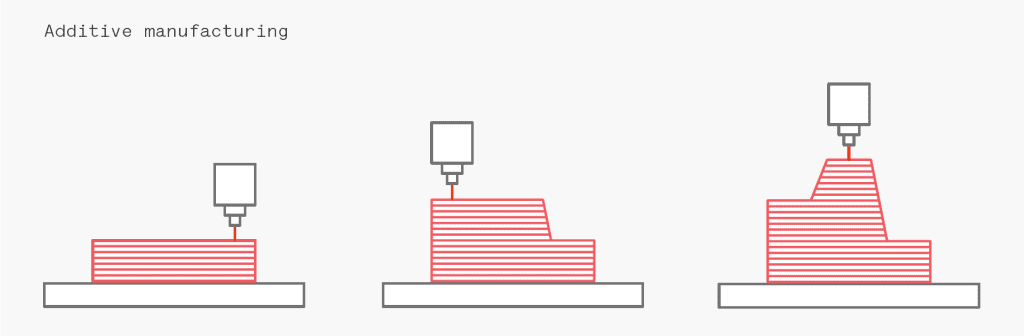
CNC machining is a kind of standard Subtractive Manufacturing technology. Different from Additive Manufacturing, CNC machining usually starts from solid blocks. Then, by measuring the parts' length, width and height and consumption, sharp rotary tools or cutters are used to cut materials to achieve the shape. CNC is a commonly used traditional processing method for mass production. It has high repeatability and accuracy and is equipped with various tool options for realizing numerous geometric shapes and processing-rich materials.
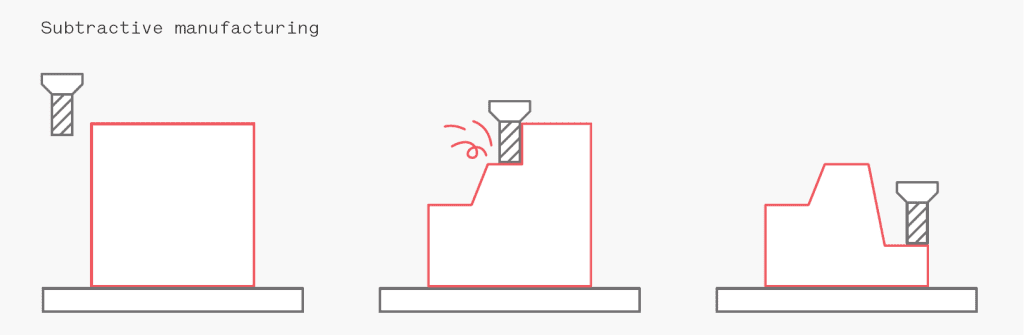
CNC machining can only process fillets with a certain radian. Therefore, it has no problem for CNC machining to process external right angles. However, it cannot directly process internal right angles, which could be realized through Electrical Discharge Machining. In addition, CNC machining curved surfaces are time-consuming; if the programmers and operators are not experienced enough, it is easy to leave apparent lines on the parts.
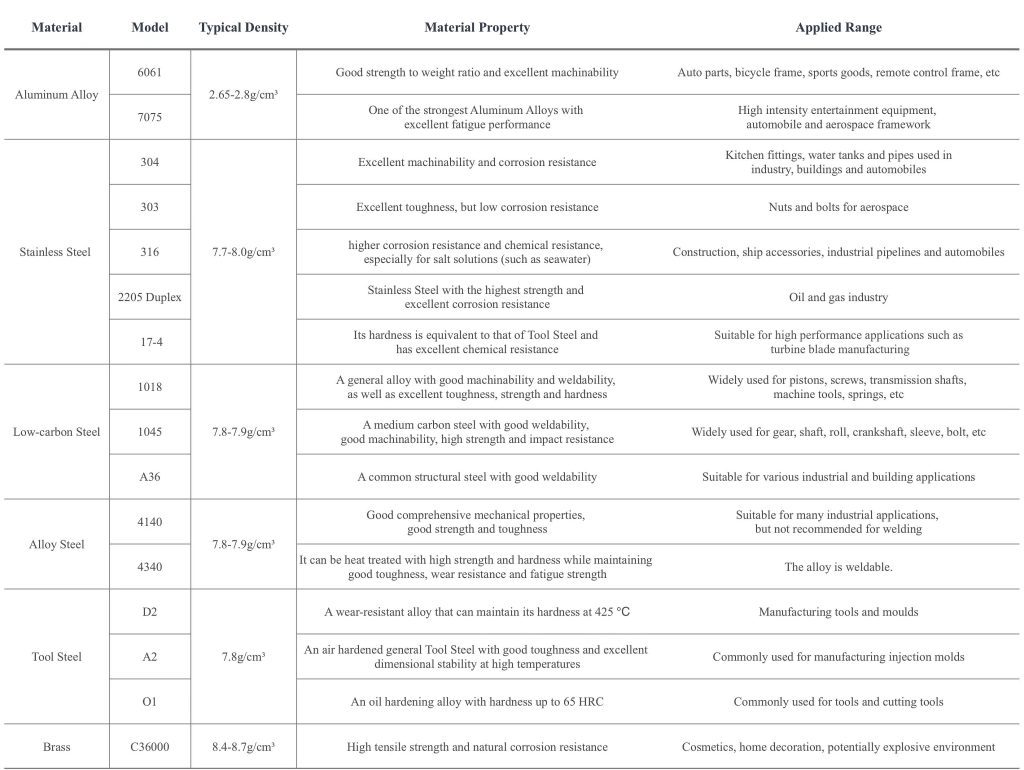
Table 2. Properties of Metal Materials and Alloy Materials Commonly Used in CNC Machining
Selecting suitable materials for CNC can be a difficult task. When choosing materials for parts or products, many factors should be considered, including machinability, price, corrosion resistance, strength, weight and appearance.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Metal 3D Printing Compared to CNC Machining?
Metal 3D Printing can provide a lightweight solution. The excellent design flexibility of Metal 3D Printing is closely related to the creation of lightweight structures. In fact, following the best design practices of Metal 3D Printing can always provide a lightweight solution. Commonly advanced CAD techniques such as topology optimization and generative design are often used for this purpose, resulting in lighter parts (typically 25% to 50%) and higher stiffness. This is the key to high-end applications such as aerospace and other industries.
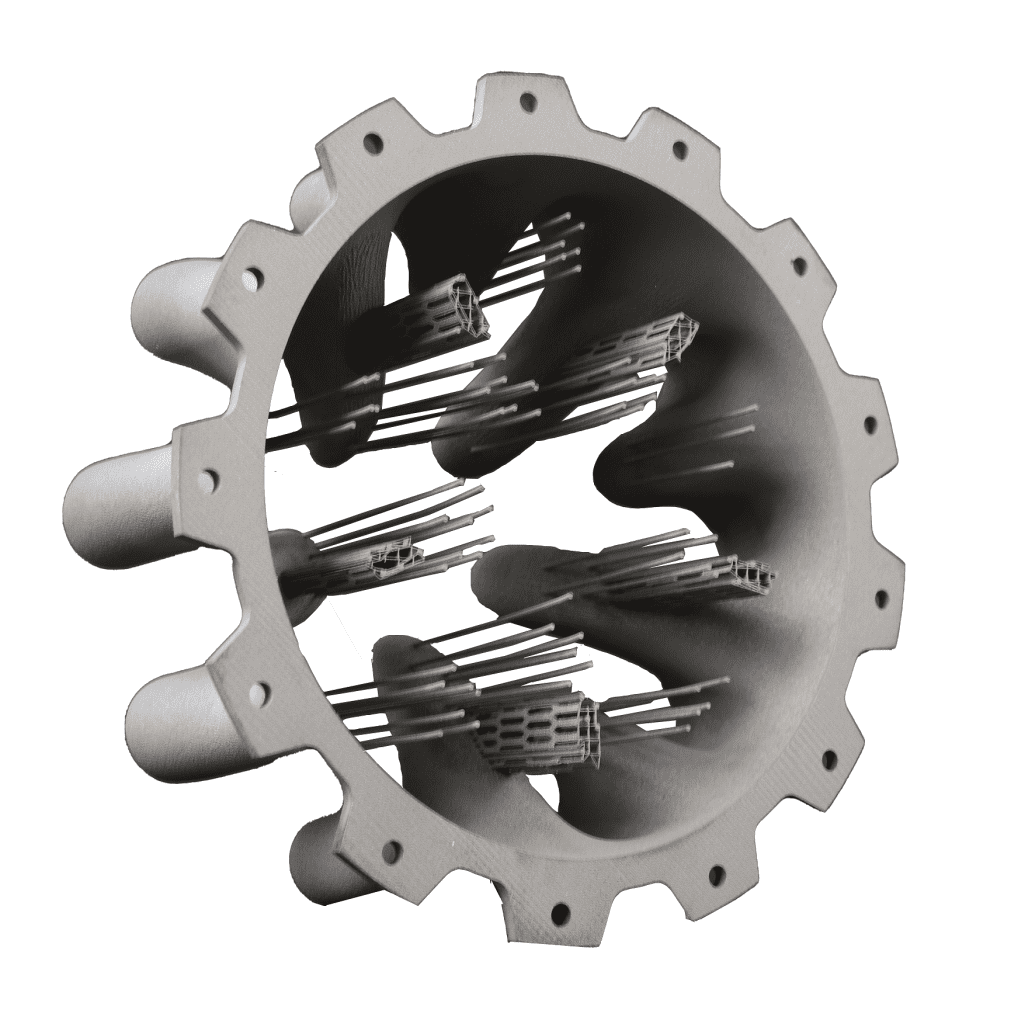
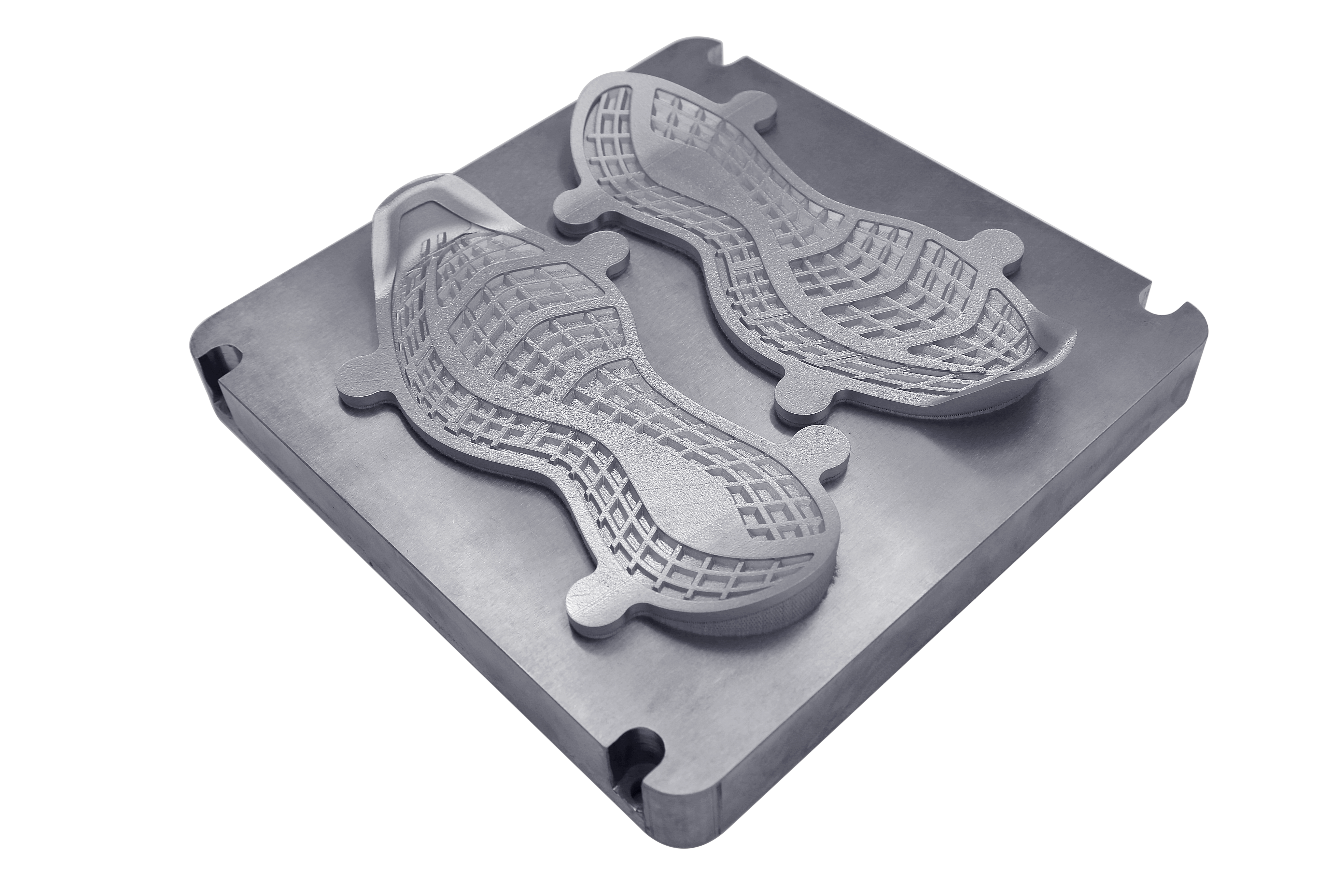
Metal 3D Printing can efficiently form more complex structures. The metal 3D printer is used to create objects layer by layer. Take the most common powder bed melting as an example; the metal powder is repeatedly dissolved and solidified bit by laser to create objects. The moulding limit is relatively small, and complex structures such as lattices can be manufactured. Therefore, some parts that cannot be de-moulded or cut by tools can be manufactured by 3D printing. In addition, the strength of metal 3D printing parts has been higher than that of casting, and with the continuous progress of technology, its strength is also approaching the forging strength.
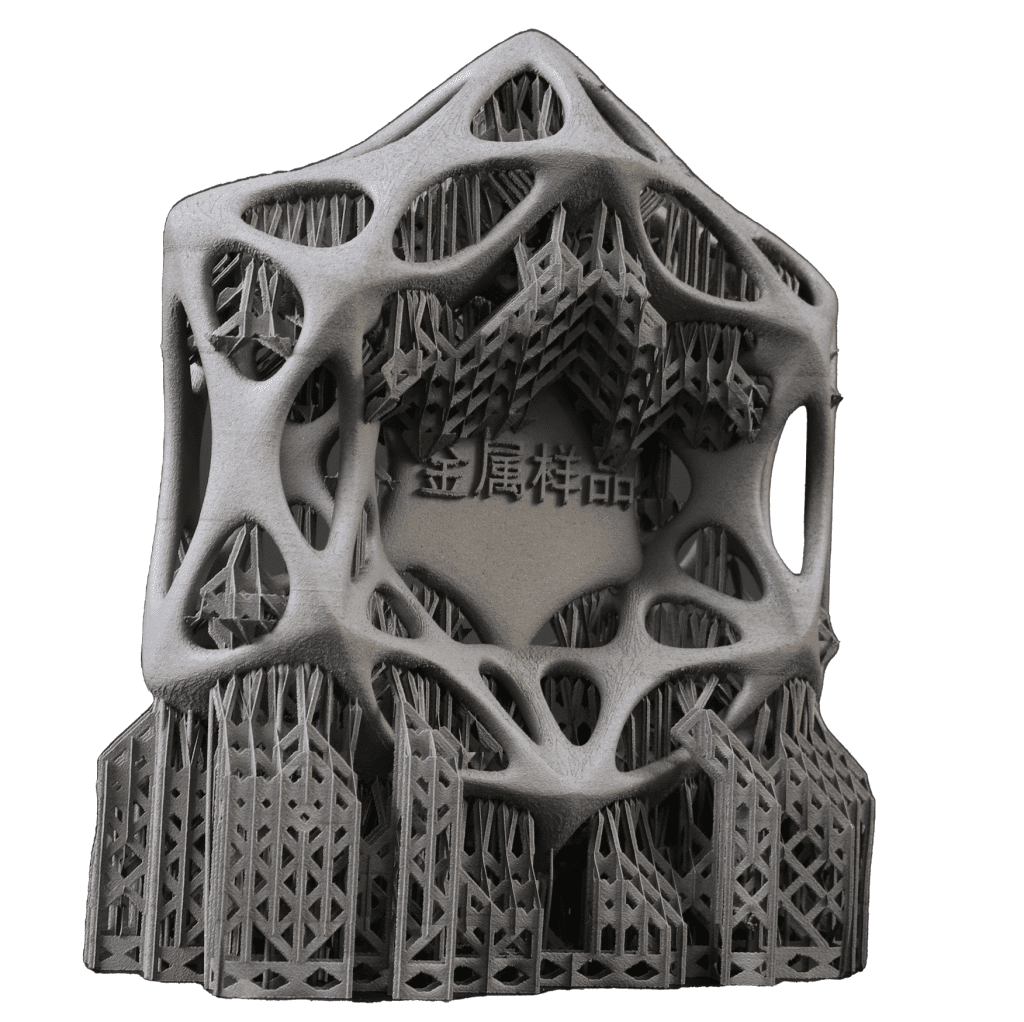

Metal 3D Printing can help reduce development costs and lead time. Compared with CNC Machining, Metal 3D Print can save a lot of materials, costly metal materials. It replaces the original solid body with a complex and reasonable structure so that the finished product has lower weight and better mechanical properties. When the number of parts is relatively small, or only one piece is needed, 3D printing has a short production time and is cheap. Therefore, Metal 3D Printing is suitable for sample or small-batch production.
Another advantage of Metal 3D Print is its ability to combine components into a single component, eliminating the need for fasteners and resulting in parts that can simultaneously provide multiple functions. In addition, labour costs and delivery time are minimized, and maintenance and service requirements are reduced. As an added benefit, reducing the total number of parts is another way to create lightweight structures.
The disadvantages of Metal 3D Printing compared to CNC Machining are:
Metal 3D Printing parts' surface finish is rougher than traditional processes, and it needs post-processing to achieve a perfect surface finish.
Metal 3D printing is not suitable for mass production. Therefore, when the production scale reaches a certain amount, the economic benefits of Metal 3D Printing will decline.
Due to thermal stress, Metal 3D Printing is not suitable for large-scale manufacturing parts at present and is prone to warping. However, the new Metal 3D Printing technology represented by jet technology has overcome the difficulty. In the future, Metal 3D Printing can also manufacture large-scale parts with the gradual popularization of technology.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of CNC Machining Compared to Metal 3D Printing?
CNC-machined parts have higher accuracy. The error on each axis is only a few microns so high surface accuracy can be achieved without additional processing. In terms of tolerance, CNC Machining is generally better than Metal 3D Printing because heat treatment and reprocessing processes are unnecessary. In addition, CNC Machining is very suitable for manufacturing heavy parts.
The surface finish of parts processed by CNC is high, and even the mirror effect can be achieved.

CNC Machining terminals are widely used and easy to purchase. Now basically all walks of life are using CNC machined parts. In addition, CNC Machining plants can purchase tools and materials from third-party Vendors.
CNC Machining is faster and cheaper for small batch parts production without the advantages of 3D printing functions such as internal flow path, complex geometry, and lightweight, merged components.
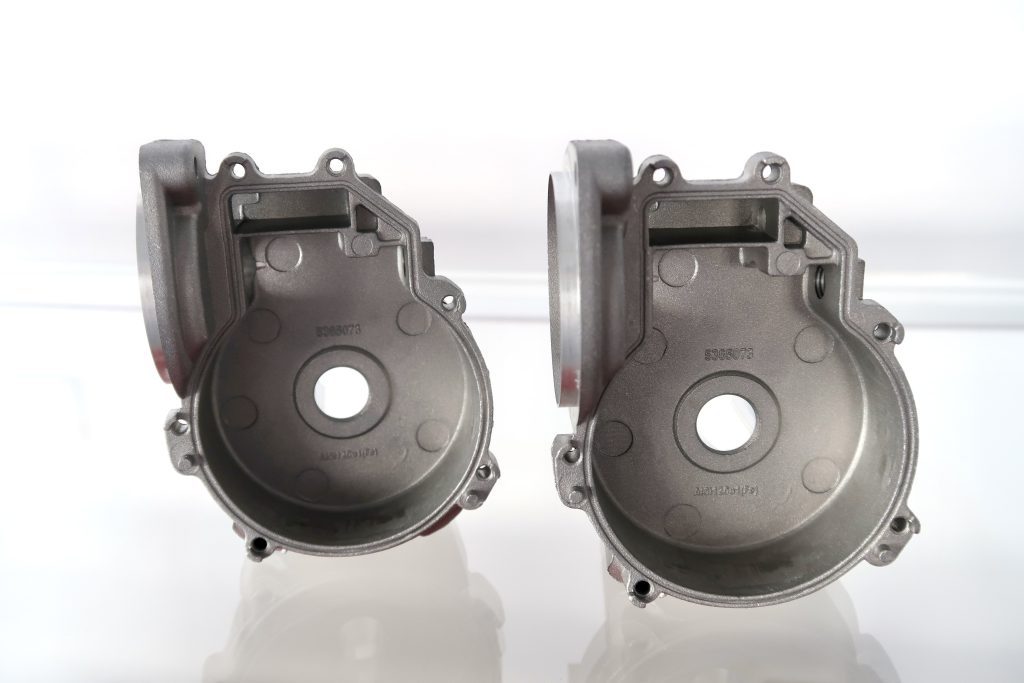

The disadvantage of CNC Machining compared to Metal 3D Printing is: CNC machining uses special cutting tools to shape parts which means the need for such tools. Another process is required to manufacture the tool without such a unique tool, such as creating an undercut. This also means that even using five-axis machining, many features of fixed parts cannot be machined. Cylindrical tools are difficult to machine "complete angles". The internal right angle needs to be realized by undercutting. Otherwise, an arc edge will appear.
What's the Best Way to Make Your Part
Economic Considerations of Metal 3D Printing and CNC Printing
If only tolerance and surface finish are considered, CNC is undoubtedly the best choice. However, Metal 3D Print has apparent advantages in consideration of cost, human resources, delivery date and other comprehensive factors. Therefore, when adopting Metal 3D Printing, factors taken into consideration include the following:
· Part size and order quantity. It is more economical to produce small-batch parts.
· Part size and design complexity. Small and medium-sized parts with medium to high complexity are ideal.
· Part surface area and frame volume. The larger the surface area per cubic inch, the more features.
Drivers include:
· Fast and efficient product delivery
· Ensure multiple design iterations are possible
· Design can be changed
Metal 3D printing and CNC Machining are complimentary
Many manufacturers believe they must choose one technology based on these advantages and disadvantages. But if their benefits are appropriately applied, they can be combined to provide more significant opportunities.
For automotive, aerospace and other high-precision products, the required tolerance of metal parts exceeds the tolerance that Metal 3D Printing can provide. However, the design flexibility provided by 3D printing (usually used for lightweight/enhanced ergonomics) is exactly what these applications require. Therefore, CNC Machining based on 3D printing parts can provide the best advantages, and in some cases, the tolerance can be as low as ± 0.005 mm.
Similarly, considering the satisfactory surface treatment of precise tolerance, especially the parts that need to be precisely matched with other parts, 3D printing can make the parts a little larger and then process them with CNC, such as 5-axis milling, to meet the accuracy requirements.
There are also advantages in materials. Previously, 3D printing could not take advantage of the mechanical properties of titanium, aluminium, Inconel and stainless steel in terms of strength, corrosion resistance and thermal performance due to the limitation of materials. In addition to these materials, more and more alloys/superalloys can be used for 3D printing and CNC machining for precision processing. Product development engineers have greater flexibility in using materials they are familiar with.


