Polyamide vs. Nylon: Are they the same?

Explore the differences between polyamide and nylon, understanding their unique properties for tailored 3D printing applications.
Introduction to Polyamide and Nylon
This introduction aims to clarify the key differences between polyamide (PA) and nylon.
Polyamide and nylon are two fundamental materials employed in numerous manufacturing processes. Known for their exceptional strength, durability, and chemical resistance.
Understanding Polyamide
Definition of Polyamide
Polyamide (PA): A class of polymers containing amide bonds (–CONH–) in the repeating units. This includes various types of synthetic and natural polyamides.
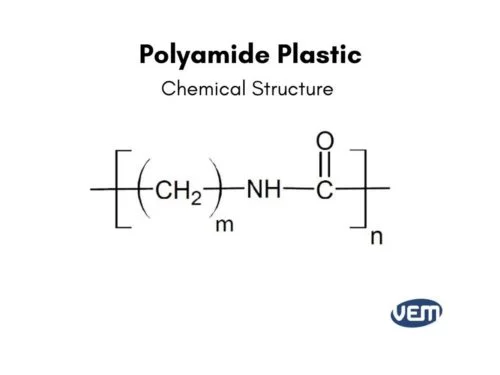
Understanding the Polyamide Family
Polyamides form a large group of plastics with similar chemical structures. While they share basic characteristics, different types of polyamides have a wide range of specific properties.
Nylon: A Prominent Member of the PA Family
Nylons, a type of polyamide, are well-known materials made through a process called condensation polymerization, which combines diamines and dicarboxylic acids.
The monomers used decide the type of nylon. For example, Nylon 6 comes from a single monomer called caprolactam, while Nylon 6,6 is made from hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.
The Diversity of Polyamides
Although nylon is a common type, it's important to understand that polyamides include a wider variety of materials.
For example, aramid fibers are high-performance polyamides known for their exceptional strength and heat resistance. Kevlar, a trade name for a specific aramid fiber, demonstrates this class of materials.
Understanding Nylon
Nylon: A specific type of synthetic polyamide. Nylon is a subset of polyamides and was the first commercially successful synthetic thermoplastic polymer.

A prominent member of the polyamide family, nylon is extensively used in 3D printing due to its desirable properties. Let's delve deeper into its characteristics.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Chemically, nylon is a polymer composed of repeating amide units. Nylon's unique structure provides it with a versatile set of properties.

Polyamides & Nylon for 3D Printing
High-Strength Polyamides
High-strength polyamides, often called engineering nylons, are designed for demanding applications that need exceptional strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials are stronger, stiffer, and more durable than standard nylons.
Common examples of high-strength polyamides used in 3D printing include:
Nylon 11 (PA11): Known for its excellent impact resistance, chemical resistance, and flexibility. Often used in automotive, oil and gas, and industrial applications.
Nylon 12 (PA12): Offers a good balance of strength, stiffness, and toughness. It's widely used in various industries due to its versatility.
Standard Nylon

Standard nylon is strong and versatile, but generally has lower mechanical properties compared to high-strength polyamides. It is often used in applications where cost-effectiveness and general-purpose performance are prioritized.
Common examples of standard nylon used in 3D printing include:
Nylon 6: A widely used and cost-effective nylon grade. Offers good strength and toughness but may not be suitable for demanding applications.
Nylon 6,6: Known for its high melting point and good chemical resistance. It's often used in industrial applications where temperature resistance is required.
PA vs. Nylon — From A 3D Printing Perspective
Mechanical Properties
Strength: High-strength polyamides are generally stronger than standard nylon types. This makes them ideal for applications demanding high load-bearing capacity.
Flexibility: Nylon often offers better flexibility than high-strength polyamides. This property is beneficial for components that require some flexibility or resilience.
Thermal Properties
Melting Point: Nylon and high-strength polyamides typically have similar melting points, which influence the 3D printing process parameters.
Heat Resistance: High-strength polyamides better withstand heat compared to standard nylons, making them suitable for high-temperature environments.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Both nylon and high-strength polyamides can achieve smooth surfaces under optimal printing conditions. However, specific post-processing techniques may be required to achieve the desired aesthetic appearance.
Printing Speed Considerations
Printing speeds can vary based on the specific nylon or polyamide type and the 3D printer used. Often, adjusting print settings is needed for the best results with different materials.
Cost Comparisons
High-strength polyamides often come with a higher price tag compared to standard nylon grades. The choice between the two materials should consider the balance between material cost and the desired performance characteristics.
Summary: Comparison Table
Property | Standard Nylon | High-Strength Polyamide |
|---|---|---|
Mechanical Properties (Strength) | Good | Superior |
Mechanical Properties (Flexibility) | Better | Lower |
Thermal Properties (Melting Point) | Similar | Similar |
Thermal Properties (Heat Resistance) | Lower | Higher |
Surface Finish | Smooth (with potential post-processing) | Smooth (with potential post-processing) |
Printing Speed Considerations | May vary | May vary |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Polyamide & Nylon Applications in 3D Printing:
Functional Prototypes
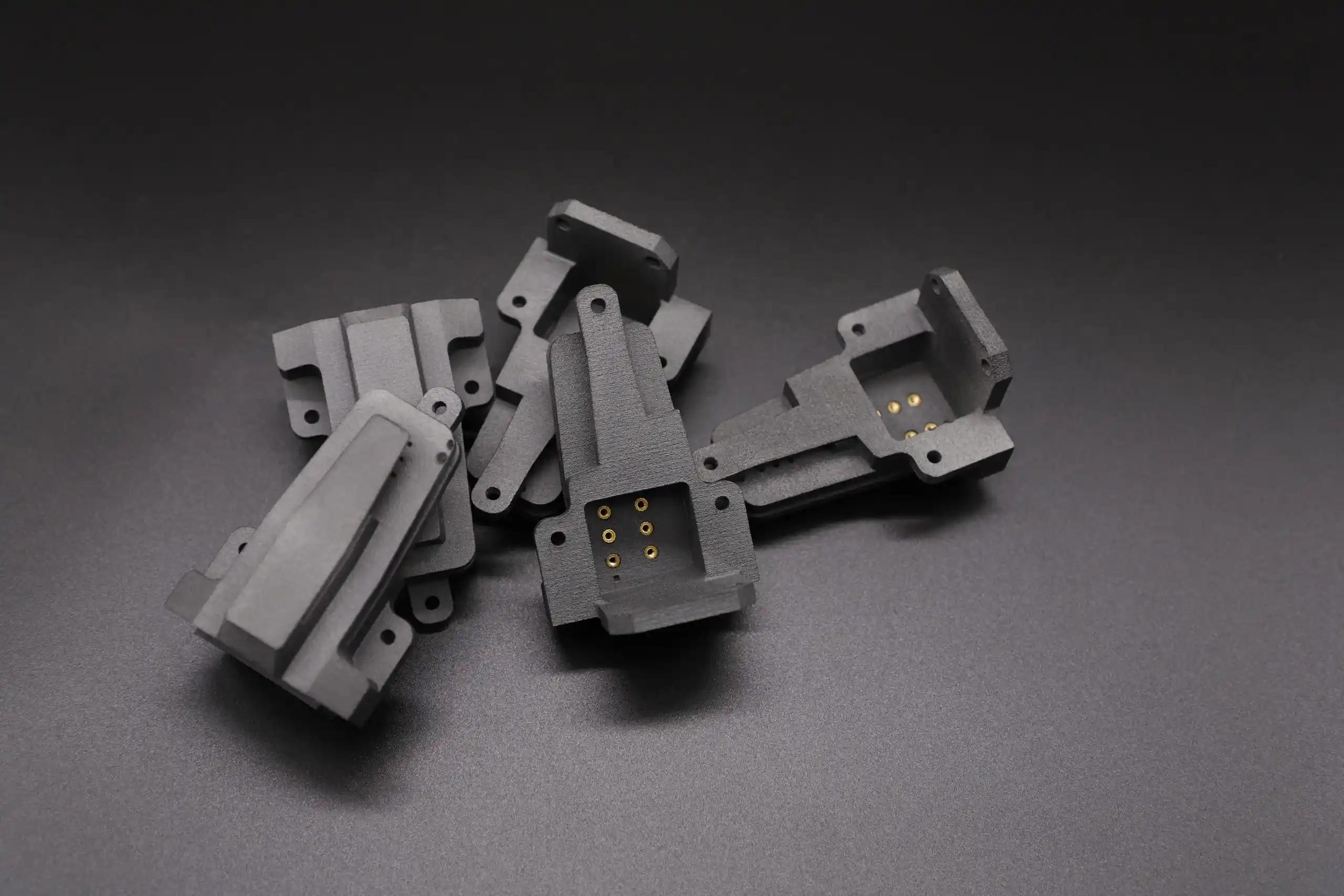

Creates robust prototypes that undergo rigorous testing, mimicking final product performance.
End-Use Parts
Manufactures strong and reliable parts for demanding applications like gears, housings, and components in automotive and aerospace.
Snap-Fit Assemblies
Enables creation of parts with tight tolerances that snap together securely, eliminating adhesives or fasteners.
Bearings and Bushings
Low friction and wear resistance make it ideal for smooth-operating bearings and bushings under load.
Tools and Jigs
Strength and durability translate to long-lasting tools and jigs for various applications.
Living Hinges
Creates flexible hinges seamlessly integrated within a printed part, eliminating separate hinges.
Consumer Goods
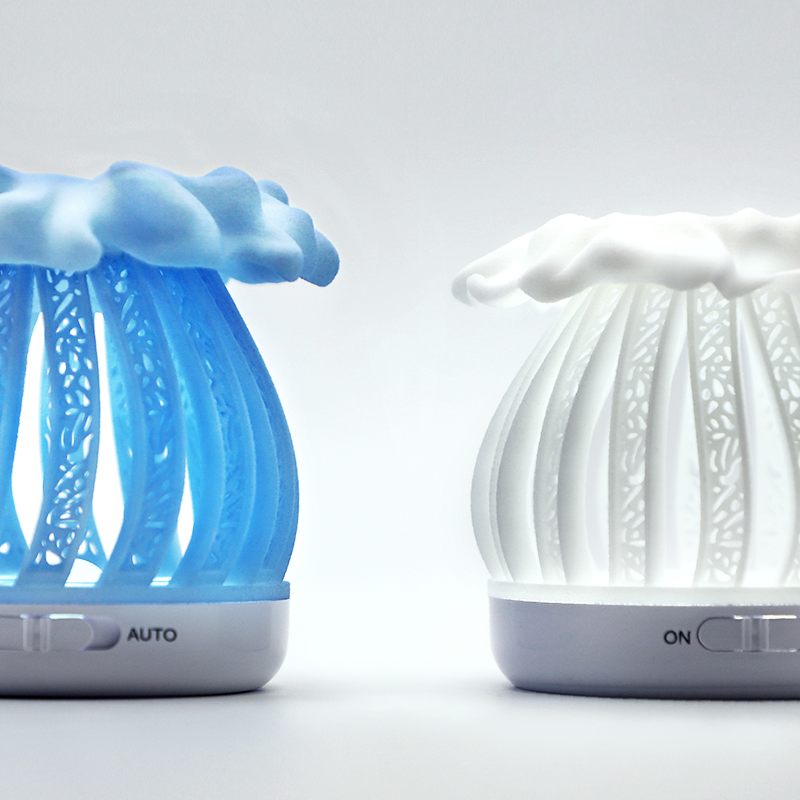

Source: Unionfab
Consumer Goods Widely used for various consumer goods due to affordability and good aesthetics, like phone cases, toys, and sporting goods components.
Wearable Applications
Flexibility makes it ideal for creating comfortable and functional wearables like bracelets or watch bands.
Conclusion
Polyamide and nylon, often used interchangeably, are distinct members of the same polymer family. This analysis has thoroughly compared their chemical composition, mechanical properties, thermal behavior, surface quality, printing speed, and cost.
Contact Unionfab today to unlock the full potential of nylon 3D printing! Empower Your 3D Printing with Unionfab's material Expertise.

