A Comprehensive Guide to Types of Fasteners
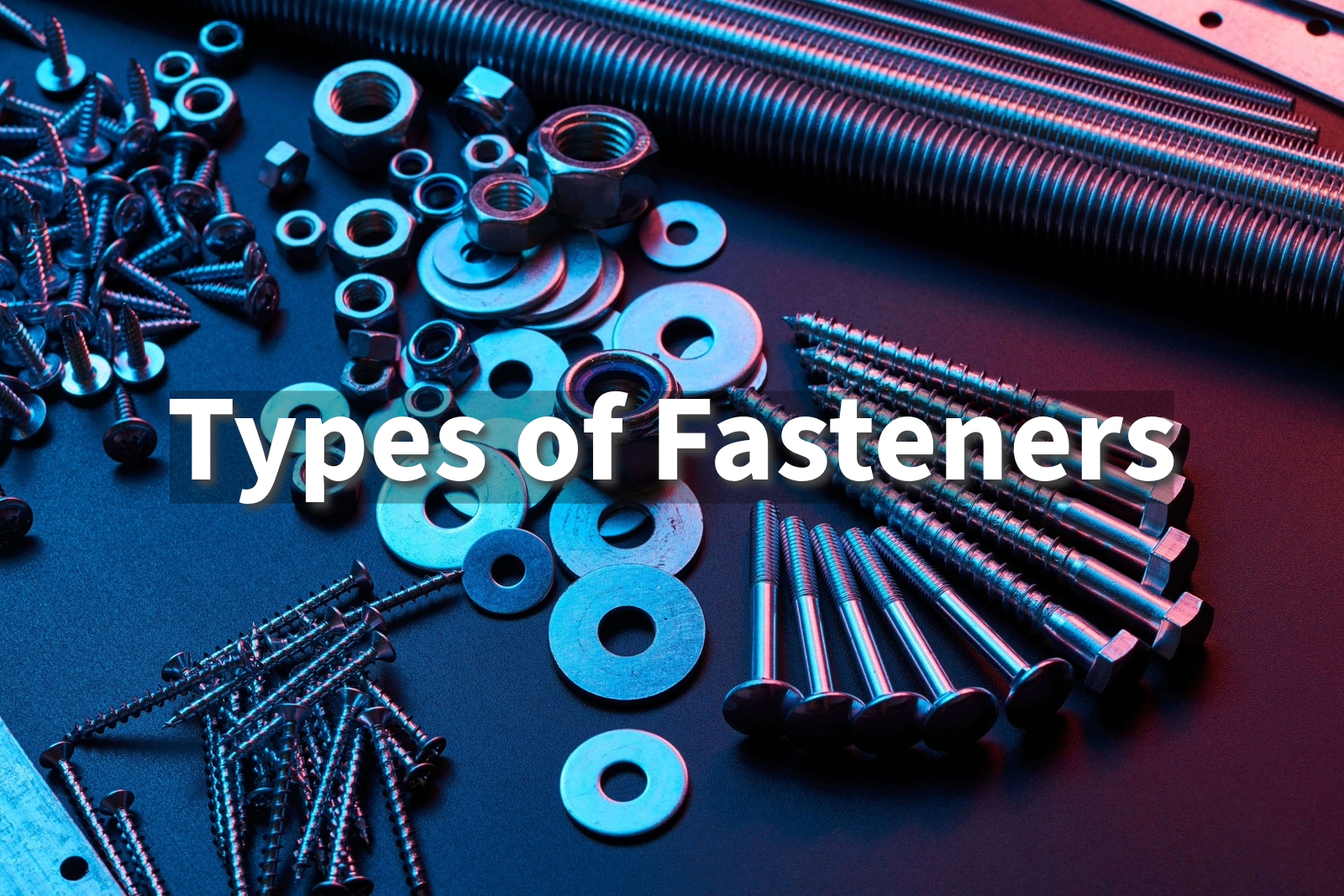
This guide explores different types of fasteners, from screws to nuts and bolts. Explore the types of fasteners and their essential role in various applications.
Introduction
Fasteners are hardware devices that mechanically join or affix two or more objects together. Some common examples of fasteners include screws, nuts, bolts, pins, and nails. Fasteners play an important role in holding together structures and mechanical systems across many industries.
Categories of Fasteners
Temporary vs Permanent Fasteners

Source: centrix-us.com

Source:marshfasteners.com
Fasteners can be categorized as temporary and permanent based on how easy it is to disconnect the joint they form.
Temporary fasteners like nuts and bolts allow disassembly with hand tools, while permanent fasteners like rivets and welds require cutting or destruction to remove.
Threaded vs Non-Threaded Fasteners
Another way to classify fasteners is by whether they have threads or not. Threaded fasteners like screws and bolts mate with a matching threaded hole or nut to form a joint.
Non-threaded fasteners like nails, pins, and press-fits form joints without the use of threads. Threaded fasteners can be tightened or loosened, while non-threaded types generally provide permanent or frictional fits.

Source: mudgefasteners.com

Source: rajalindustries.com
Common Types of Fasteners
Bolts
Bolts are an anchoring type of threaded fastener used with nuts. They come in many types - carriage bolts have a square shoulder, lag bolts are long with a single point, and machine bolts are used in precision equipment.
Bolts are made of steel, stainless steel or specialty alloys. They distribute pressure across large areas in structures, machinery and construction.
Screws
Wood screws and sheet metal screws are often drive in by screwdrivers or powered drivers. Machine screws are smaller threaded fasteners used in assemblies. Self-tapping screws can directly thread into thin metal or plastic. Phillips, flathead and Robertson drives are common screw head styles.
Nuts
Nuts come in various styles like hex, wing, acorn to tighten with spanners or wrenches. Nuts tightened against the threads of bolts and rods secure assemblies and apply clamping force across components. Self-locking nuts have nylon inserts to prevent loosening from vibration.
Washers
Washers protect components from damage and distribute clamping loads evenly. They are often used under bolt heads and nuts.
Lock washers have teeth that inhibit loosening through vibration. Flat, fender, and spring washers are some other types.
Rivets
Rivets fasten aircraft skins and fuselages permanently. They are also used in shipbuilding, bridges and manufacturing.
Rivets are driven and bucked, then the protruding end is crushed to grip components securely. This makes for lightweight, high-strength integral joints.
Specialty Fasteners
Anchors
Wall anchors are used to attach objects to drywall or masonry. They come in expanding and threaded types. Concrete anchors embed into cured concrete and distribute load across its surface. These resist pulling forces in walls, floors and foundations.
Clips & Clamps
Cable clips restrain wires and pipes. Hose clamps join flexible tubes. Retaining clamps hold objects together for alignment. E-clips and panel clips mount components internally. U-clips attach vinyl trim pieces. Spring clamps are used in sheet metal fabrication.
Snap Rings & Retaining Rings
Circlips or snap rings with open or closed ends are self-locking fasteners inserted into grooves. They retain bearings, gears, pulleys and shafts from axial movement. E-rings and C-rings are common retaining ring varieties used in motors, transmission shafts and more.
In conclusion, this guide covered basic to specialized fasteners used across industries. Proper fastener selection ensures structural integrity and reliability in all applications. Let me know if any area needs more explanation.
Choosing the Right Fastener
When selecting fasteners for a project, some key considerations are:
Materials
Fasteners must be compatible with the base materials they join. Stainless or coated steel resists corrosion when joining dissimilar metals or for exterior/wet use. Alloys like brass or nylon work well for plastics.
Loads
Bolt size, thread engagement length and tightening torque must exceed anticipated tensile, shear and vibration loads. Calculate load ratings based on fastener dimensions and material properties.
Environment
Corrosion resistance is critical for conditions involving chemicals, salts or moisture. Heat resistance is needed for high temperature surroundings. Those functioning underwater or buried require waterproofing.
Specific Projects
For furniture, use wood screws or nails. Sheet metal assemblies need self-tapping screws. Machinery benefits from hex bolts tightened to spec. Aircraft builders rely on aerospace-rated fasteners. Construction calls for lag bolts, concrete anchors and panel pins.
By evaluating the installation factors above on a case by case basis, the most appropriate fasteners for securely and reliably joining different projects can be chosen from the many available types and sizes. Proper fastening ensures structural integrity and safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this guide has provided an overview of the many types of fasteners that exist and their important applications across industries. From common screws, bolts and nuts, to specialty anchors, clips and rings - fasteners perform the critical function of joining other components together reliably.
Whether used permanently or temporarily, threaded or non-threaded, the choice of suitable fasteners is key to engineering safe and durable assemblies.
For any project, taking time to consider factors like material compatibility, load requirements and the operating environment will help select fasteners that properly fulfill the intended purpose.
Choosing hardware based on industry standards or manufacturer recommendations when available ensures structural integrity. Fasteners are often simple parts but importance to the success of designs cannot be understated.
Trust Unionfab for Quality Solutions!
At Unionfab, we understand that selecting the correct fastener is crucial to the success of your project.
Whether you're working with complex machinery, precision tools, or large-scale industrial builds, the quality of your fasteners can make all the difference.
Get an instant quote or contact Unionfab now to discuss your requirements and discover how our advanced manufacturing capabilities can bring your vision to life.

