Discover the Key Advantages of Additive Manufacturing

Understand why additive manufacturing is revolutionizing industries with its ability to create complex parts, reduce costs, and accelerate prototyping.
Introduction
Additive Manufacturing (AM), also known as 3D printing, is a modern technology that creates objects by adding material layer by layer. Unlike traditional methods that cut away material, AM builds parts from the ground up, making it very efficient and precise.
AM is becoming more important in many industries today. Companies in areas like aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and even consumer goods are using AM to make parts faster, with less waste, and in more complex designs. This technology is changing how products are made, leading to new innovations that weren't possible with traditional manufacturing methods.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Source: Unionfab
Additive Manufacturing (AM) is a process of creating 3D objects by adding material layer by layer using a digital design. This method is different from traditional manufacturing, which usually involves cutting or shaping materials. AM allows for more freedom in design, less material waste, and the ability to create complex shapes that are hard to achieve with regular techniques.
AM started in the 1980s with early 3D printing technologies, which were mainly used for making prototypes. Over time, AM has greatly improved and is now used to make finished products. Today, it's used in many areas, like aerospace for lightweight parts, healthcare for custom medical implants, automotive for rapid prototyping, and consumer goods for personalized items.
Different Types of Additive Manufacturing
There are several types of Additive Manufacturing technologies, each suited for different applications:
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
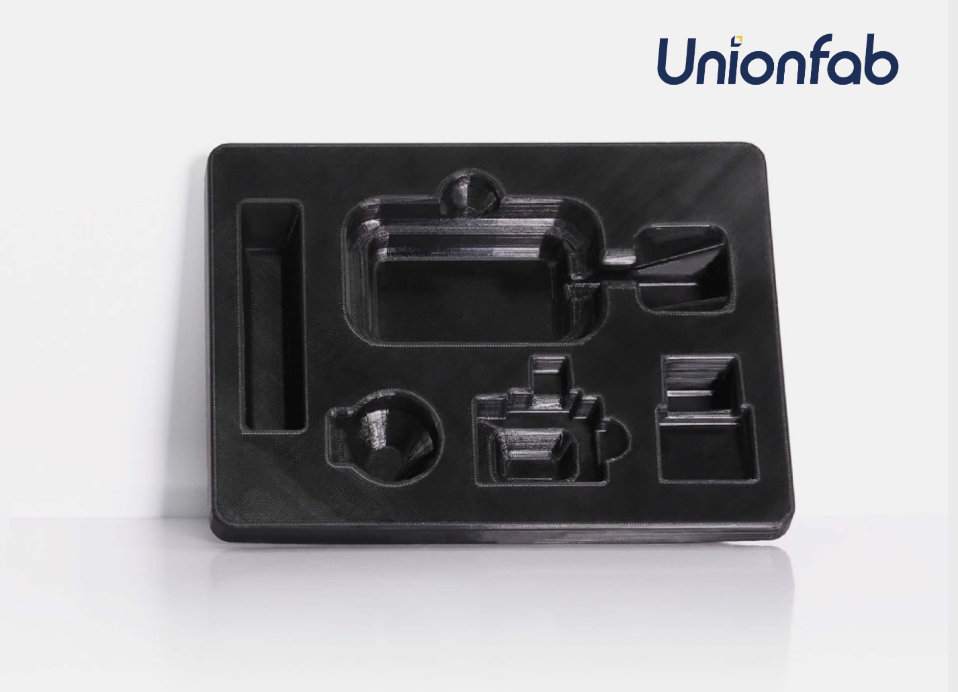

Source: Unionfab
FDM is one of the most common types of 3D printing. It works by melting a plastic filament and laying it down layer by layer to create an object. FDM is often used for prototyping and making simple parts because it is affordable and easy to use.
Stereolithography (SLA)

Source: Unionfab
SLA uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers, building up the object. It is known for creating parts with very high detail and a smooth surface finish, making it ideal for applications like dental molds or jewelry prototypes.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)

Source: Unionfab
SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered material, like nylon, into solid parts. This method is great for making durable, functional parts and is often used in aerospace and automotive industries.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
DLP is similar to SLA but uses a digital light projector to cure the resin. It can be faster than SLA and is used for detailed and high-quality parts in industries like healthcare and consumer goods.
Metal Additive Manufacturing

Source: Unionfab
Metal AM, such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM) or Electron Beam Melting (EBM), uses lasers or electron beams to fuse metal powder into solid parts. This type is used for high-performance applications in aerospace, automotive, and medical implants where strong, durable metal parts are needed.
Binder Jetting
Binder jetting involves depositing a liquid binding agent onto a powder bed to create layers. It can be used with metals, ceramics, or sand, and is often used for making molds, casting, or full-color prototypes.

Advantages of Additive Manufacturing
Customization and Design Freedom
AM allows for detailed designs and highly customized parts. This is especially helpful in healthcare, where custom implants and prosthetics are made to fit each patient perfectly, and in aerospace, where complex parts can be created to improve performance.
Rapid Prototyping
AM makes prototyping much faster compared to traditional methods. This lets designers and engineers quickly test and improve their designs, speeding up product development and getting products to market faster.
Cost-Effectiveness
AM creates less material waste compared to traditional methods, making it cost-effective, especially for small production runs. This is useful in industries that need custom or small-batch production, reducing the costs related to traditional tools and setups.
Reduced Lead Times
AM can produce parts much faster, which means shorter production times. This helps manufacturers respond quickly to changes in demand, which is important for industries that need fast turnaround times.
Material Efficiency and Sustainability
AM generates less waste because material is added only where needed. This makes production more sustainable. Also, many AM processes can use recyclable materials, making them even more environmentally friendly.
On-Demand Manufacturing
AM allows for parts to be made as needed, which reduces the need for large inventories. This flexibility is great for small-batch production, spare parts, and custom orders, making manufacturing more efficient and cost-effective.
Applications of Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing is used in many industries, each benefiting from its unique capabilities.
In aerospace, AM is used to make lightweight parts that help improve fuel efficiency and lower emissions. It allows for complex shapes that are hard or impossible to create with traditional methods, resulting in stronger and lighter components.

Example of AM in Aerospace industry - Pure Copper Exhaust Nozzle
Source: UnionfabIn healthcare, AM is transforming the production of custom medical implants and prosthetics. The ability to create patient-specific models allows for better-fitting devices, improving patient comfort and outcomes. AM is also used to make surgical tools and even experimental tissue structures.

Source: Unionfab
In the automotive industry, AM is used for rapid prototyping and making custom parts. It helps designers quickly test and improve new ideas, which shortens the design cycle. AM is also used for making specialized parts in small quantities, often needed for high-performance or classic vehicles.

Example of 3D Printed Car Air-Conditioning
Source: Unionfab
Conclusion
Additive Manufacturing offers many advantages, like customization, rapid prototyping, cost-effectiveness, shorter production times, material efficiency, and on-demand production. These benefits are changing industries like aerospace, healthcare, and automotive by allowing innovative designs, faster production, and more sustainable practices.
FAQs
What are the main advantages of additive manufacturing?
The main advantages are customization, rapid prototyping, cost-effectiveness, shorter production times, material efficiency, and on-demand manufacturing.
How does additive manufacturing reduce production costs?
It reduces costs by minimizing material waste, allowing for small production runs, and reducing the need for expensive tools.
What industries benefit most from additive manufacturing?
Industries like aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and consumer products benefit a lot because they need complex and custom parts.
Is additive manufacturing environmentally friendly?
Yes, it is more environmentally friendly than traditional methods because it creates less material waste and uses recyclable materials.
What are the limitations of additive manufacturing?
Some limitations include high machine costs, limited material choices, and challenges in keeping quality and consistency in some applications.
Unionfab: Additive Manufacturing Solutions
Unionfab delivers expert 3D printing solutions tailored to your project's exact needs. Our advanced manufacturing combines:
Cutting-edge 3D printing, CNC, molding and casting technology
Custom engineering
Rapid production (7-12 days)
Cost-effective prototyping
ISO-certified quality
From concept to creation, we turn your ideas into reality with unmatched precision and efficiency.
Get in touch with Unionfab today, or acquire your free quote instantly online— let’s make your ideas a reality.

