The Complete Guide to Face Milling

Explore face milling in depth: learn what a face mill is, how the face milling process works, different types of cutters, and best practices for efficient CNC machining.
Introduction
What is Face Milling and Why is it Important?
Face milling is a type of milling operation in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining. It involves cutting a flat surface, called the "face," on a workpiece to make it smooth. In face milling, a tool with rotating cutting edges moves across the workpiece, shaving off thin layers.
Face milling is important because it is efficient and versatile. It helps prepare surfaces for further work and makes parts have exact dimensions and smooth finishes. By learning how face milling works, you can make better decisions about tools and settings, which will improve the process and the quality of the final product.
What is a Face Mill?
Definition of a Face Mill
A face mill is a cutting tool used in milling to create flat surfaces. It has multiple cutting edges (or inserts) mounted on a rotating tool body. These inserts can be replaced when they wear out, making face mills flexible and cost-effective. The main purpose of a face mill is to remove a lot of material quickly and leave a smooth finish.
Types of Face Mills
There are different types of face mills, each good for different tasks:
Indexable Face Mills: These have cutting inserts that can be replaced when they wear out, making them easy to maintain and flexible. They are often used for removing material quickly.
Solid Carbide Face Mills: These are made from a solid piece of carbide, which makes them very precise. They are used when accuracy and rigidity are very important.
Face Mill vs. End Mill
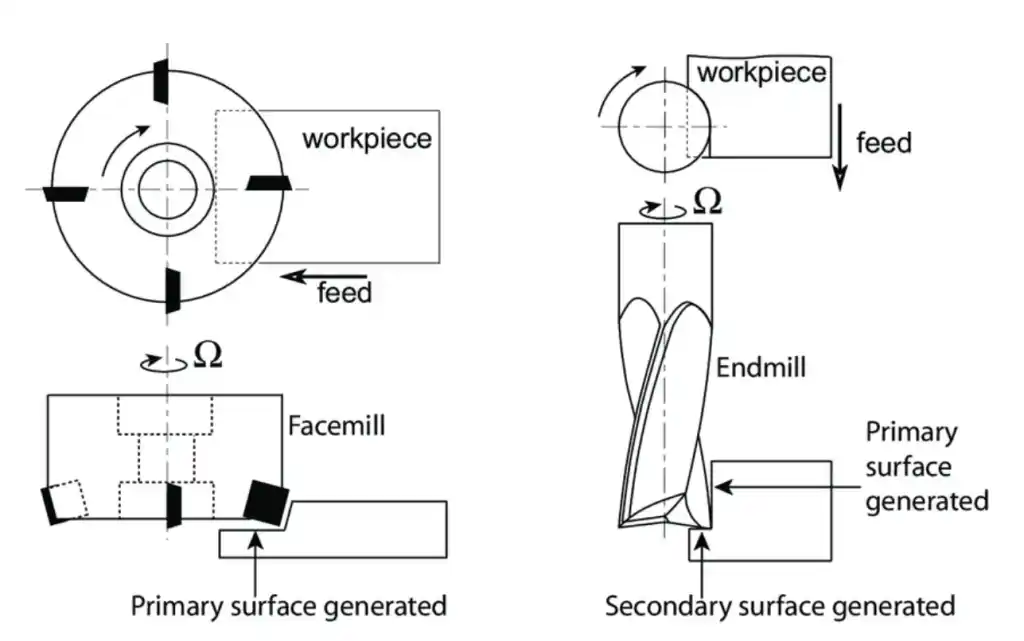
Source: samhotool.com
Face mills and end mills are both used in CNC machining, but they are used for different purposes:
Face Mill: Used to cut large, flat surfaces. It has multiple cutting edges, making it efficient for quickly removing material.
End Mill: Used for more detailed work, like cutting slots or making contours. It has cutting edges on the side and the tip, making it more versatile.
Understanding the Face Milling Process
How Face Milling Works
Face milling uses a cutting tool that rotates and removes material from a workpiece to create a flat surface. The cutting tool is placed perpendicular to the workpiece and moves across the surface in a controlled path. The setup of the tool, the type of inserts, and the cutting parameters are important for getting a smooth finish. Proper setup helps improve accuracy and efficiency.
Types of Face Milling Operations
There are two main types of face milling operations:
Conventional Milling: The cutter rotates against the direction of the feed. This is often used for roughing operations because it gives better control over the cutting force.
Climb Milling: The cutter rotates in the same direction as the feed. This is preferred for finishing because it produces a smoother surface and causes less wear on the tool.
Applications of Face Milling
Face milling is used in many industries, including:
Automotive: For machining engine parts and other components that need precise flat surfaces.
Aerospace: To machine flat surfaces on aircraft components.
Mold Making: To create smooth surfaces on molds and dies, ensuring a good fit for molded parts.
Types of Face Milling Cutters
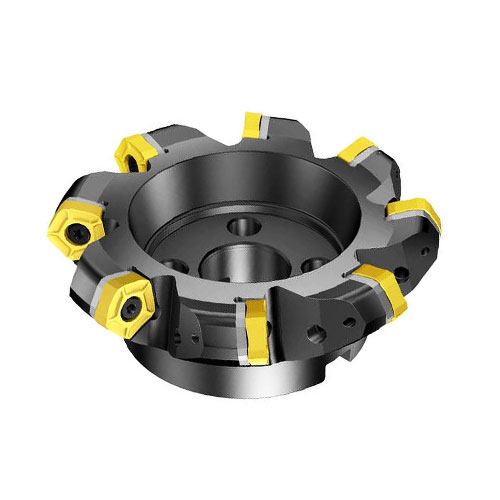
Indexable Face Milling Cutters

Source: dictoolsindia.com
Indexable face milling cutters have replaceable inserts that can be changed when they wear out. This makes them cost-effective since only the inserts need to be replaced. They are commonly used for removing large amounts of material efficiently.
Solid Carbide Cutters

Source: maydown.co.uk
Solid carbide cutters are made entirely from carbide, making them very durable and precise. They are used for smaller workpieces and where vibration needs to be minimized for a smooth finish.
Ceramic and CBN Cutters

Source: ntkcuttingtools.com
Ceramic and Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) cutters are used for high-speed milling. Ceramic cutters are resistant to heat, so they are used to cut hard materials. CBN cutters are used for very hard steels. Both types are wear-resistant and can improve productivity in tough applications.
Face Milling Parameters
Depth of Cut, Feed Rate, and Speed
Choosing the right milling settings is key to getting a good finish and extending tool life:
Depth of Cut: This is how deep the tool cuts into the material. Softer materials can handle a deeper cut, while harder materials need a shallower cut to prevent tool damage.
Feed Rate: This is how fast the cutting tool moves across the workpiece. Higher feed rates can speed up the process but may lower surface quality. Finding the right balance is important.
Cutting Speed: This is how fast the cutting edge moves through the material. Different materials require different cutting speeds to avoid overheating or damaging the tool.
Choosing Proper Insert Geometry
The shape and edge of the inserts affect how well the milling operation works:
Insert Shape: Inserts can be round, square, or triangular. The shape depends on the type of milling and the desired finish. Round inserts are good for heavy cuts, while square inserts provide more stability for finishing.
Edge Design: The edge of the insert affects cutting forces. Positive rake inserts reduce cutting forces, making them ideal for softer materials. Negative rake inserts are more durable and used for harder materials.
Face Milling vs. Peripheral Milling
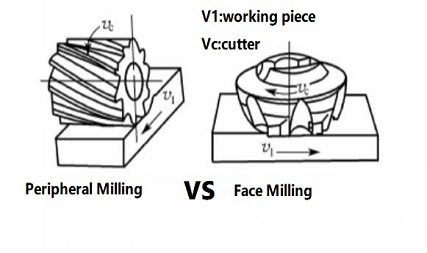
Source: worthyhardware.com
Definition and Key Differences
Face milling and peripheral milling are two common types of milling:
Face Milling: The cutting tool is perpendicular to the surface, and the edges on the face of the tool create a flat surface.
Peripheral Milling: The cutting tool is parallel to the surface, and the edges on the side of the tool remove material to create slots or contours.
Face milling is used for machining flat surfaces, while peripheral milling is used for cutting along the edges to create features like slots.
Applications and Use Cases
Face Milling: Used for making smooth, flat surfaces on large workpieces, like preparing surfaces for further machining.
Peripheral Milling: Used for cutting deep slots or creating complex shapes and edges.
Advantages and Limitations
Face Milling:
Advantages: High material removal rate, good for large flat surfaces, and capable of a smooth finish.
Limitations: Not ideal for cutting deep features or complex shapes.
Peripheral Milling:
Advantages: Good for creating complex shapes and detailed features.
Limitations: Slower material removal compared to face milling and may require more complex paths.
Advantages and Limitations of Face Milling
Benefits of Face Milling
Face milling has several benefits:
Smooth Surface Finish: It produces very smooth and high-quality surfaces.
High Material Removal Rate: It can remove a lot of material quickly, making it efficient.
Versatility: It can be used on many different materials and surfaces.
Challenges and Limitations
There are some challenges with face milling:
Chip Management: Managing the chips produced during milling can be difficult, especially for materials that make long chips.
Tool Wear: The cutting edges wear out, especially when cutting hard materials, requiring regular replacement.
Vibration: Vibration can affect the quality of the surface and increase tool wear if the setup is not rigid.
Best Practices for Successful Face Milling
Tool Selection and Set Up
Choosing the right tool and setting up the machine correctly is important for success:
Tool Selection: Choose a face mill with inserts that suit the material. Use indexable cutters for fast material removal and solid carbide cutters for precision.
Machine Set Up: Make sure the machine is stable to avoid vibration. Proper alignment helps achieve a smooth finish.
Optimal Milling Strategies
To get the best results, follow these strategies:
Step-Over Strategies: Use an optimal step-over distance to ensure even material removal. A smaller step-over gives a finer finish, while a larger one increases productivity.
Adjust Cutting Speeds: Adjust the cutting speed based on the material to prevent tool damage.
Consistent Depth of Cut: Keep the depth of cut consistent to ensure even material removal.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Avoid these common mistakes for better results:
Incorrect Tool Engagement: Make sure the cutting tool is properly engaged with the workpiece.
Improper Cutting Speed: Using the wrong speed can cause overheating or poor surface quality. Adjust the speed for each material.
Poor Insert Choice: Choose the right insert geometry for the material. Using the wrong insert can lead to poor performance.
Safety Considerations in Face Milling
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always use proper safety gear during face milling. Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying chips, gloves to protect your hands, and hearing protection if the machine is loud. Also, wear proper clothing and shoes to avoid injuries.
Machine Safety
Follow these machine safety practices to avoid accidents:
Make sure the workpiece is securely clamped to prevent movement.
Keep all machine guards in place and know where the emergency stop buttons are.
Never reach into the machine while it is running, and always check the tool paths before starting to avoid collisions.
Conclusion
Face milling is an important machining process for creating flat, smooth surfaces. To succeed with face milling, it's essential to understand the different types of tools, choose the right settings, and follow best practices. By using proper safety measures and avoiding common mistakes, you can achieve efficient, high-quality results in your face milling operations.
Choose Unionfab for Your CNC Needs
At Unionfab, we provide state-of-the-art CNC machining services that ensure precision, quality, and efficiency. Whether you're looking for advanced face milling solutions or comprehensive CNC services, our expert team is ready to assist.
Contact us at Unionfab to learn more about how we can support your next project. Let us help you achieve exceptional results with our professional CNC machining services.


