What is Alodine? [+ Applications & Benefits]
![What is Alodine? [+ Applications & Benefits]](https://ufc-dtc-cms.oss-accelerate.aliyuncs.com/blog/20250320/215028_al67cuqh6.png)
Learn everything about Alodine conversion coating—how it enhances corrosion resistance, maintains electrical conductivity, and improves adhesion for aluminum parts.
Introduction
Importance of Surface Treatment
In industrial manufacturing, metal components are often exposed to environmental conditions that cause corrosion, oxidation, and wear. This is especially true for aluminum and magnesium alloys, which, despite their lightweight and strength, are susceptible to environmental degradation over time.
To enhance durability, improve adhesion for coatings, and maintain performance, surface treatments like Alodine conversion coating play a crucial role. These treatments provide a protective layer on the metal surface, extending the lifespan of components and ensuring consistent functionality in various applications.
Why Alodine Matters
Alodine is widely used for aluminum and aluminum alloys. It provides corrosion resistance while preserving electrical conductivity, making it an essential solution for industries like aerospace, automotive, military, and electronics.
Additionally, Alodine treatment acts as an effective primer layer, improving the adhesion of paint, powder coatings, and other protective finishes. Given its versatility and cost-effectiveness, Alodine remains one of the most commonly used conversion coatings in precision-engineered manufacturing.
What is Alodine?
Definition
Alodine, also known as chromate conversion coating, is a chemical treatment applied to metal surfaces—primarily aluminum and magnesium alloys—to form a thin, protective oxide layer. This enhances corrosion resistance and improves adhesion for paints and primers. Unlike anodizing, which significantly alters the material’s surface properties, Alodine treatment is a low-impact process that retains the metal’s electrical conductivity while adding a durable protective layer.
Historical Background
The development of chromate conversion coatings dates back to mid-20th century, primarily for military and aerospace applications. The need for lightweight but corrosion-resistant materials led to the widespread adoption of Alodine, particularly in aircraft structures and defense equipment.
Over the years, environmental concerns regarding hexavalent chromium (Cr⁶⁺) led to advancements in trivalent chromium (Cr³⁺) coatings, which provide similar levels of protection while being more environmentally friendly. Today, both traditional Alodine coatings and RoHS-compliant alternatives are widely used across various industries.
How Alodine Works
Chemical Reaction
Alodine treatment involves a chemical reaction between the metal surface and chromate-based solution:
The metal surface is thoroughly cleaned and prepared to remove contaminants.
The part is exposed to a chromate solution, which contains hexavalent or trivalent chromium.
A chemical reaction occurs, forming a protective oxide film that enhances corrosion resistance.
The part is then rinsed and dried, locking in the Alodine coating for long-term durability.
Coating Properties
Thickness: Typically 0.00001 - 0.00004 inches, ensuring minimal dimensional change.
Color: Varies from gold, brown to clear, depending on the formulation.
Conductivity: Unlike anodizing, Alodine maintains electrical conductivity.
Corrosion Resistance: Provides moderate but effective protection, making it ideal for aerospace and electronics applications.
Types of Alodine
MIL-DTL-5541 Type 1 (Hexavalent Chromium)
Traditional formulation containing hexavalent chromium.
Gold or brown color, providing easy identification.
Strong corrosion resistance, widely used in aerospace and military applications.
Regulated due to environmental concerns in certain regions.
MIL-DTL-5541 Type 2 (Trivalent Chromium)
RoHS-compliant and environmentally friendly.
Clear or light yellow color, making it a preferred choice for modern industries.
Lower corrosion resistance than Type 1 but still effective for many applications.
Increasingly used in aerospace, electronics, and consumer industries.
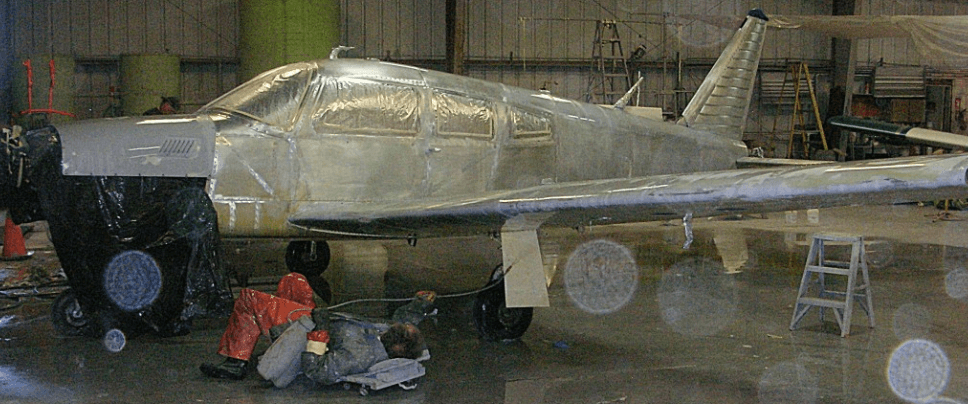
Aerospace Industry

Source: kracon.com
Aircraft fuselage components require effective surface treatments to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Alodine conversion coating is widely used in the aerospace industry to enhance corrosion resistance while maintaining the lightweight nature of aluminum structures.
This protective layer ensures that the fuselage remains resistant to oxidation, improving durability and extending the operational lifespan of the aircraft. Additionally, Alodine-treated components serve as an excellent primer for further coatings, such as paint or additional protective finishes, ensuring long-term reliability in extreme atmospheric conditions.
Electronics Industry
Source: richconn-cnc.com
In the electronics industry, Alodine conversion coating is crucial for ensuring the durability and functionality of sensitive components. Many circuit board enclosures and shielding components are treated with Alodine to protect against corrosion while maintaining excellent electrical conductivity. This is particularly important in RF and EMI shielding applications, where the material must provide a continuous conductive path for proper grounding.
Additionally, Alodine-treated aluminum parts are commonly used in electronic enclosures, power distribution units, and aerospace electronics, ensuring reliable performance even in harsh environments. By preventing oxidation and improving adhesion for secondary coatings, Alodine helps manufacturers maintain the integrity of precision electronic assemblies.
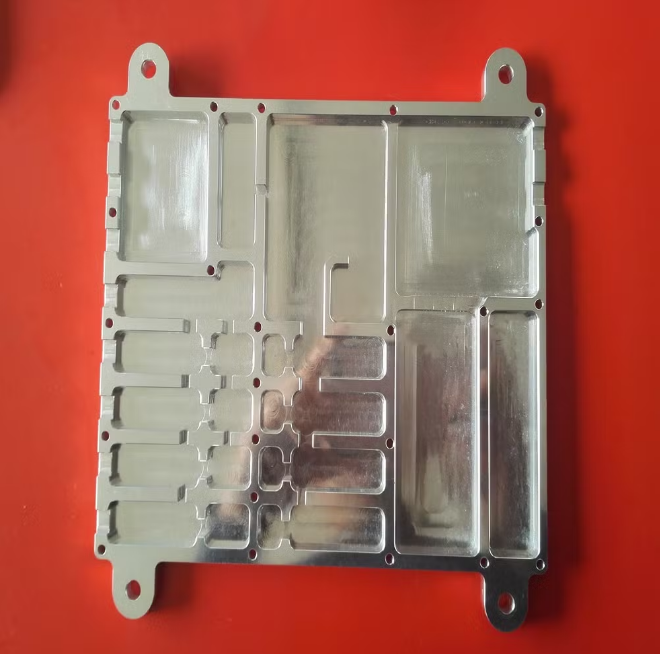
Automotive Industry

Source: wuxiderf.en.made-in-china.com

In the automotive industry, Alodine conversion coating plays a critical role in protecting chassis components from corrosion, especially in environments exposed to moisture, road salts, and temperature fluctuations. By forming a thin, protective layer on aluminum and other lightweight metals, Alodine extends the lifespan of structural components while maintaining their mechanical integrity.
This treatment is particularly beneficial for electric vehicle battery enclosures, heat exchangers, and drivetrain housings, where maintaining lightweight properties and durability is crucial. Furthermore, Alodine improves paint adhesion, making it an excellent preparatory step before additional coatings or protective finishes are applied.
Advantages of Alodine
✅ Excellent corrosion resistance – Prevents oxidation in harsh environments.
✅ Maintains electrical conductivity – Ideal for electronic components.
✅ Simple application process – Room-temperature treatment.
✅ Cost-effective – Lower cost than anodizing or plating.
✅ Good paint adhesion – Works as a primer layer for further coatings.
✅ Fast processing time – Quick turnaround compared to other treatments.
Limitations of Alodine
❌ Lower wear resistance – Not as durable as anodizing.
❌ Limited color options – Typically gold, brown, or clear.
❌ Environmental regulations – Hexavalent chromium is restricted in many industries.

Alodine vs. Other Surface Treatments
Below are detailed comparisons between Alodine and other common surface treatments.
Alodine vs. Anodizing
Aspect | Alodine | |
|---|---|---|
Process | Chemical conversion coating | Electrochemical oxidation |
Coating Thickness | 0.5 – 4 µm (thin) | 5 – 25 µm (thicker) |
Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, good as a primer | High, excellent for harsh environments |
Electrical Conductivity | Conductive | Insulating (except Type III) |
Durability | Basic, not wear-resistant | Hard, highly wear-resistant |
Color Options | Clear, gold | Wide range of dyed colors |
Environment & Safety | Contains hazardous hexavalent chromium (unless trivalent) | More eco-friendly, but acid waste needs treatment |
Summary
Alodine is thin, conductive, and mainly used for corrosion protection and primer applications. Anodizing provides a much harder, more durable, and decorative finish but reduces conductivity.
Alodine vs. Powder Coating
Aspect | Alodine | |
|---|---|---|
Process | Chemical conversion | Electrostatic powder + heat curing |
Coating Thickness | 0.5 – 4 µm (thin) | 50 – 150 µm (thicker) |
Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent, long-lasting protection |
Electrical Conductivity | Conductive | Non-conductive |
Durability | Basic | High impact and wear resistance |
Color & Finish | Limited, gold/clear | Wide range, including glossy & matte |
Environment & Safety | Contains chromium | Eco-friendly, low VOCs |
Summary
Alodine is thin and conductive but lacks durability. Powder coating is much thicker, more protective, and available in various colors but is non-conductive.
Alodine vs. Galvanizing
Aspect | Alodine | |
|---|---|---|
Process | Chemical conversion | Zinc coating via hot-dip/electroplating |
Coating Thickness | 0.5 – 4 µm | 50 – 150 µm |
Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Very high, especially outdoors |
Electrical Conductivity | Conductive | May reduce conductivity |
Durability | Basic | High, but zinc layer can wear off |
Appearance | Clear, gold | Matte gray, sometimes spangled |
Environment & Safety | Contains chromium | Requires proper handling for zinc fumes |
Summary
Alodine is best for aluminum and electrical applications, while galvanizing offers superior corrosion resistance for steel, especially in outdoor environments.
CNC Machining & Finishing Services by Unionfab
At Unionfab, we provide precision CNC machining services with compatibility for Alodine and other surface treatments. Our services include:
✅ Surface treatment compatibility (anodizing, plating, powder coating, and more)
✅ High-precision CNC milling, turning, and engraving
✅ Support for multiple materials (aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, etc.)
✅ Fast turnaround & instant quoting system
Get a free CNC machining quote today! Visit our CNC service page to learn more.
Conclusion
Alodine is a versatile, cost-effective surface treatment that enhances corrosion resistance and conductivity while maintaining minimal impact on part dimensions. With applications across aerospace, automotive, electronics, and defense, it remains a preferred choice for many industries.
When selecting a surface treatment for CNC machined parts, consider your specific application needs—whether it’s corrosion resistance, conductivity, or wear resistance. If you need high-quality CNC machining, Unionfab offers expert services to help you achieve the best results.
Not sure which surface treatment is right for your project? Contact Unionfab today for expert consultation and CNC machining solutions!


