3D Print Ghosting[+Causes, Fixes & Modern Solutions]

Fix ghosting in 3D prints with expert tips! Learn causes, pro fixes, and smart tech for clean, pro-quality prints every time.
What is 3D Print Ghosting
Ghosting (also called ringing or echoing) is a 3D printing defect where faint ripples or repeated patterns appear on the surface of a printed part, usually around sharp corners or features like holes and letters. These are unintended echoes of the original shape and result in a loss of print quality and surface definition.

Common symptoms:
Wavy lines near text or holes
Echo patterns following sharp edges
Smooth curves that ripple instead of staying consistent
What Causes Ghosting
Cause | Description |
|---|---|
Mechanical Oscillations | After a rapid directional change (like at a corner), the printhead or bed can overshoot and oscillate, causing waves. |
High Print Speeds | Printing too fast increases vibration and inertia, especially on unsupported or heavy axes. |
Loose Belts | Slack in belts leads to delayed or imprecise movements, worsening ghosting. |
Frame Flexing | Weak or unstable frames can absorb and reflect vibration. |
Acceleration and Jerk Settings | High values cause abrupt motion changes, triggering oscillations. |
Heavy Printhead/Bed | Heavier parts take longer to stop, contributing to ringing artifacts. |
Solutions to Eliminate or Reduce Ghosting
Fix | How It Helps |
|---|---|
Lower Print Speed | Reduces inertia and mechanical vibrations. Start with 40–60 mm/s. |
Tighten Belts | Ensure X and Y belts are firm but not overly tight. |
Reduce Acceleration & Jerk | Adjust in firmware or slicer (e.g., acceleration: 500–1000 mm/s², jerk: 5 mm/s). |
Upgrade to Rigid Frame | Metal frames or braces improve mechanical stability. |
Install Dampers | Stepper motor dampers or vibration-isolating feet absorb oscillations. |
Use Input Shaping | A firmware-level solution that cancels out mechanical vibrations. |
Best Practices to Avoid Ghosting in 3D Printing
1. Optimize Printer Mechanics
Tighten Belts Properly: Belts on X and Y axes should be firm, not floppy or overly tight.
Check for Loose Parts: Secure all screws, especially those on the stepper motors, pulleys, and frame joints.
Lubricate Linear Rails/Rods: Smooth motion helps reduce vibration and mechanical friction.
Add Frame Braces: Install diagonal supports or upgrade to aluminum extrusions for rigidity.
2. Tune Motion Settings
Reduce Print Speed: Start with 40–60 mm/s for standard prints. Lower if issues persist.
Lower Acceleration
Adjust Jerk/Junction Deviation
3. Use Advanced Firmware Features
Input Shaping (Klipper): Use an accelerometer and configure input_shaper to cancel vibration harmonics.
Pressure Advance/Linear Advance:
Helps with corner sharpness and flow control, reducing visible ghosting.
Use K-factor tuning for Marlin (M900 K0.05) or pressure_advance for Klipper.
4. Minimize Moving Mass
Use Lightweight Direct Drive Systems: Avoid bulky extruders; pancake-style motors are preferred.
Switch to Bowden if Needed: Lower moving weight at the cost of some retraction precision.
Shorten Printhead Wiring: Heavy, dangling cables can destabilize motion.
5. Stabilize the Printer Setup
Place Printer on a Stable, Heavy Table: Avoid vibrations from shaky desks.
Add Weight to the Base: Cement tiles or steel plates under the printer help dampen vibration.
Use Anti-Vibration Feet: Silicone or rubber feet absorb external vibrations.
6. Use Diagnostic Prints
Run Ringing Test Models: These show exactly how vibrations behave on your printer.
Measure Frequency with Accelerometer (if using Klipper): Helps find the optimal input shaping settings.
Print in Different Orientations: Rotate part 90° and observe ghosting pattern changes — helps diagnose axis-specific issues.
7. Smart Design & Slicing
Avoid Sharp Features When Possible: Chamfer or round edges to reduce sudden motion changes.
Enable “Outer Before Inner Wall”: Reduces ghosting on external walls.
Add Wipe or Coasting Settings (with caution): Helps smooth surface transitions, particularly in Bowden setups.
Summary Table
Area | Best Practice |
|---|---|
Mechanics | Tight belts, frame bracing, smooth linear motion |
Motion Settings | Low speed, acceleration, jerk/junction deviation |
Firmware | Input shaping, pressure advance/linear advance |
Hardware | Reduce moving mass, stabilize base |
Testing | Run ringing tests, use accelerometer (if available) |
Design | Round corners, adjust slicer order and coasting |
Advancements: How Modern Tech is Solving Ghosting
Modern firmware and motion systems offer smart solutions to ghosting without sacrificing speed:
Input Shaping (Klipper)

Source: reddit.com
Input Shaping is a technology that allows 3D printers to print faster while keeping the print quality high. Klipper firmware is currently the most popular and user-friendly platform for using this technology.
Here’s how it works:
Uses an accelerometer to monitor mechanical vibrations of the printer during motion.
Automatically adjusts motion paths to cancel out vibration-caused ghosting.
Enables fast, high-quality prints with minimal ghosting.
Pressure Advance / Linear Advance

Source: geekering.com
When a 3D printer changes speed, the filament flow inside the nozzle lags behind, causing pressure build-up or drop. This leads to common print defects like blobs, stringing, and ghosting.
Pressure Advance (Klipper) and Linear Advance (Marlin) predict these speed changes and adjust filament flow in advance:
Increases extrusion slightly before speeding up, and decreases it before slowing down.
Keeps filament flow in sync with nozzle movement.
Improves line sharpness, reduces artifacts, and enhances overall surface quality.
CoreXY & Lightweight Designs
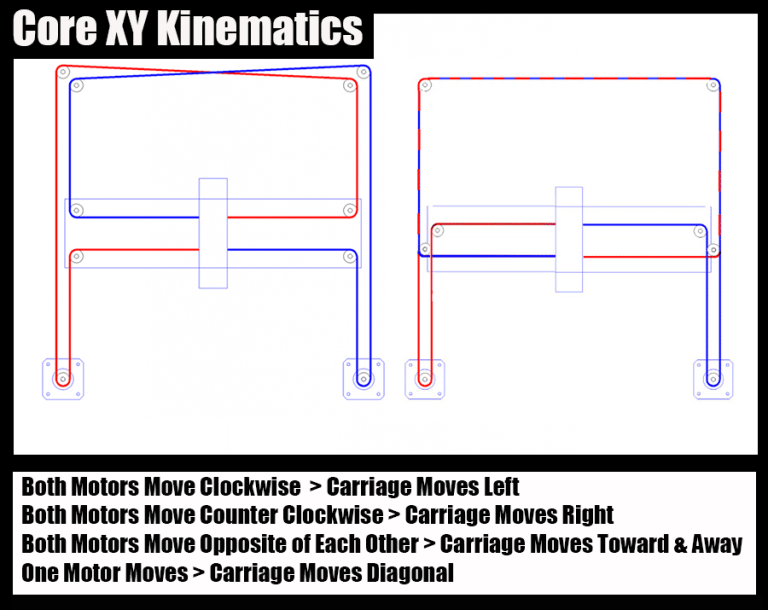
Source: 3ddistributed.com
CoreXY is a motion system that uses two motors working in tandem to move the printhead along the X and Y axes. This system allows for fast, precise movements.
When paired with lightweight components (like compact extruders and linear rails), it helps reduce moving mass and mechanical vibrations.
Reduces ghosting caused by rapid directional changes.
Offers smoother, faster, and more stable printing performance.
Tired of Ghosting? Trust Unionfab to Get It Right
Ghosting is fixable—but it takes time and might slow down your project. Therefore, outsourcing your prjoect to an experienced and reliable provider like Unionfab is well worth considering.
Whether you’re prototyping, testing, or manufacturing end-use parts, Unionfab, as China's largest 3D printing manufacturer, is committed to delivering quality professional services to ensure your parts look as good as they perform. Do not hesitate and feel free to contact us now.

FAQs
What is ghosting in printing?
Ghosting is a printing defect where faint, repeated patterns or lines appear on the surface, usually caused by mechanical vibrations or sudden direction changes.
What does ghost gun mean on 3D printer?
A "ghost gun" refers to a firearm that is 3D printed or assembled from parts without a serial number, making it untraceable and often unregulated.
Which 3D technology eliminates ghosting?
Technologies like Input Shaping (commonly used with Klipper firmware) and CoreXY motion systems help reduce or eliminate ghosting by minimizing vibrations and improving motion control.

