Multi-Color 3D Printing: All Things You Need to Know

Discover how multi-color 3D printing can transform your projects. Learn about techniques, materials, and applications for vibrant, detailed prints.
Introduction to Multi-Color 3D Printing
For years, single-color printing has been the mainstay of 3D printing technology. However, recent advancements now allow users to create objects in a rainbow of colors.
Why Multi-Color Printing is Gaining Popularity
There are several reasons why multi-color 3D printing is becoming increasingly popular. Here are a few of the key benefits:
Eye-Catching Appeal: Multi-color printing makes 3D objects more attractive by adding a variety of colors. This makes them more visually interesting and engaging, which is particularly useful for creating realistic models, prototypes, and marketing materials.
Clearer Communication: Using multiple colors in 3D printing helps to highlight specific features, differentiate components, and convey the design more effectively. This is especially helpful for making medical, engineering and architectural models easier to understand.
Unleashing Creativity: Multi-color printing allows for greater creativity by bringing ideas to life with stunning detail and vibrant colors. This is great for artists, designers, and anyone who wants to create unique and personalized objects.
The Basics of Multi-Color 3D Printing

Multi-color 3D printing goes beyond the limitations of single-color printing by incorporating multiple colors into the printing process. There are two main approaches to achieving this:
Combining filaments or materials of different colors.
Jetting or selectively curing photoreactive resins in various colors.
The specific method used depends on the printing technology employed. No matter the printing method used (filament mixing or jetting), color control relies on slicing software.
It essentially tells the printer how to combine or position the materials to achieve the exact color scheme you designed.
Different Methods to Achieve Multi-Color Prints
PolyJet Printing for Multi-Color Prints

Think of it as an advanced inkjet printer: PolyJet uses tiny droplets of liquid resins (like colored inks) to build objects layer by layer. These printers offer incredible detail and a wide range of colors for highly accurate results.
This process is fast and clean. The resins harden instantly with UV light, allowing for rapid printing with crisp layers.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM is popular for its affordability, and it can also be used for multi-color prints. Here are three FDM approaches:
1. Single Extruder with Filament Switching
2. Multi-Extruder Systems

These printers have multiple "inkjet heads" (called extruders) that deposit different colors at once, creating smoother transitions.
3. Color Mixing Techniques
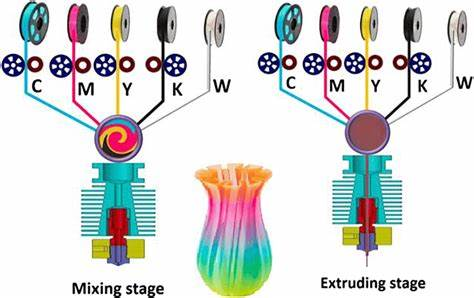
Some FDM printers have special nozzles that blend colors within the machine, offering a wider color range.
Binder Jetting for Multi-Color Printing
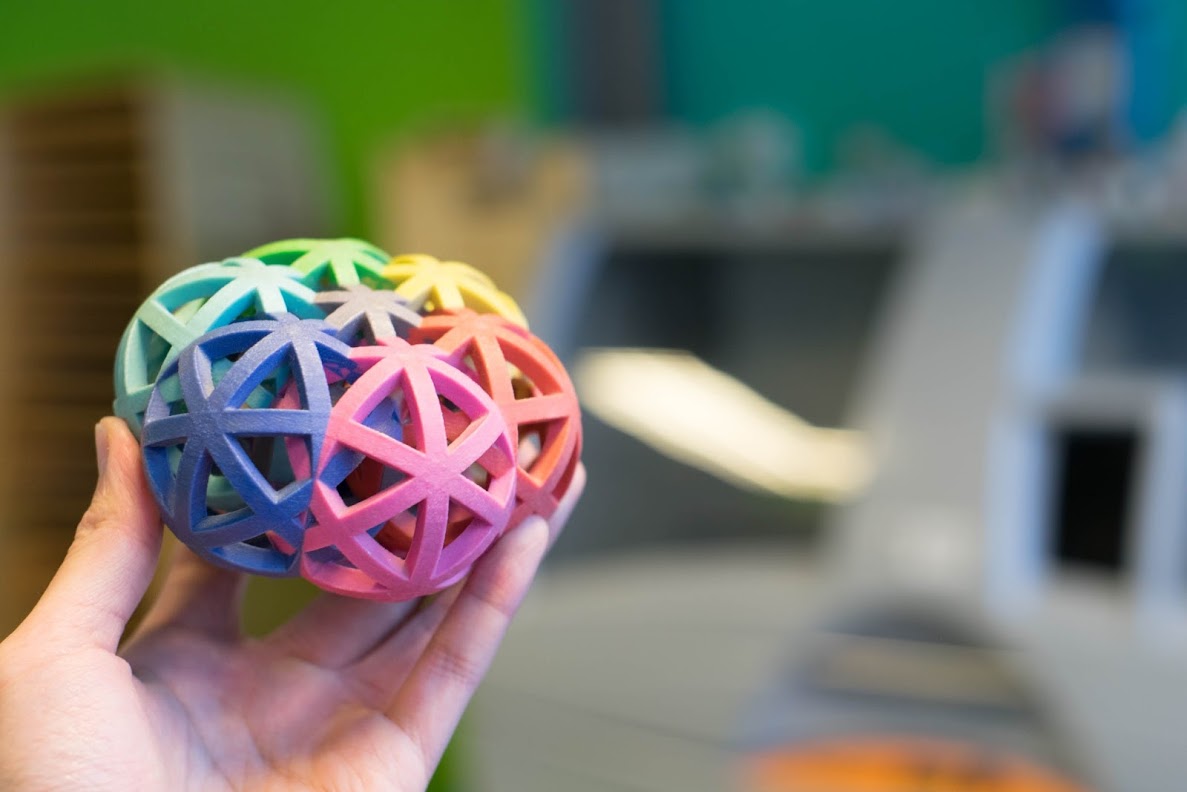

In binder jetting, a thin layer of powder, like gypsum, sand, or metal, is spread on the build platform. A print head then sprays a liquid binder onto specific areas of the powder, solidifying it to create each layer of the object.
For multi-color printing, the binder includes pigments or dyes, allowing for detailed, full-color prints.
Other Approaches to Multi-Color 3D Printing
For technologies like SLA, DLP, and SLS, painting after printing is more common for achieving multi-color effects. Here’s why:
SLA/DLP
SLA and DLP technologies typically use single-color resins, and while you can switch resin colors between prints, the color options are still limited. They do not offer dynamic color mixing during printing. Multi-color objects would generally need to be painted post-printing.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
SLS primarily uses white or gray nylon powders (often PA12) for industrial applications. The idea of "colored powders" isn't typical.
Multi-color printing in SLS is generally achieved through post-processing methods like dyeing or painting after the print is complete, not during the print.
MultiJet Fusion (MJF)
HP’s MJF does have a specialized color model (HP Jet Fusion 580/380), which uses color agents in the process, but it's not the standard version of MJF.
The majority of MJF prints are in grayscale, and color options are added post-process (e.g., dyeing).
Materials for Multi-Color 3D Printing
PolyJet Materials

PolyJet printing uses special materials called multi-color resin.
In PolyJet 3D printing, multi-color resin technology allows for the creation of highly detailed, colorful parts. The process involves the use of liquid photopolymer resins that are stored in multiple cartridges, each containing a different color or material. These resins are jetted onto the build platform in tiny droplets, similar to how an inkjet printer works.
PolyJet resins offer a vast array of colors, material properties, and surface finishes, catering to a wide range of applications.
FDM Materials
FDM printing, the most common type of 3D printing, can also do multi-color prints.

Here are some of the most popular FDM materials for multi-color prints:
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
This is a popular choice because it's easy to use, doesn't smell much, and is eco-friendly.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
This material is strong and durable, making it good for objects that need to be tough.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
This combines the ease of use of PLA with the strength of ABS, making it a great all-rounder.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
This is a flexible material, perfect for printing bendy objects.
Binder Jetting Materials
Gypsum-based powders are the primary material used in binder jetting for multi-color printing. This material, also known as sandstone, is ideal for creating vivid, detailed models.
Advantages: Gypsum-based powders are perfect for aesthetic applications, offering a broad range of colors and smooth surface finishes. They’re cost-effective and widely used for visual models, art, and architectural designs.
Limitations: They are brittle and lack the strength required for functional parts. These models are mostly used for display purposes, such as concept models or figurines.
Pros and Cons of Different Materials
Material | Technology | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
PLA | FDM | Easy to print, broad color range | Less durable |
ABS | FDM | Strong and durable | Challenging to print, limited color variety |
PETG | FDM | Strong and flexible, moderate color choices | Difficult multi-extruder use |
TPU | FDM | Flexible and durable | Challenging for multi-color prints |
Photopolymer Resins | PolyJet | High detail and color accuracy | Expensive, requires careful handling |
Gypsum-based Powders | Binder Jetting | cost-effective, smooth surface | brittle, lack the strength |

Deep Dive into PolyJet 3D Printing
PolyJet 3D printing is like an advanced inkjet printer for building 3D objects. Instead of ink, it uses special liquid plastics called photopolymers. These come in various colors and can be rigid, flexible, or even transparent.
How PolyJet 3D Printing Works
The intricate process of PolyJet 3D printing involves several key steps:
Sliced Model & Materials: A 3D model gets sliced into thin layers. The printer loads various resins (rigid, flexible, transparent) for building and support.
Jetting & Curing: Multiple nozzles jet precise droplets of resin onto the platform. A UV light instantly cures each layer.
Layer by Layer: This process repeats, building the object with specific materials based on the sliced data.
Support Removal: Finally, the easily removable support material is taken away, revealing the finished 3D object.
Advantages of PolyJet Printing
PolyJet 3D printing offers several distinct advantages over other 3D printing technologies:
High Resolution and Detail: PolyJet printers can achieve incredibly fine layer heights, resulting in exceptionally high-resolution prints with sharp details and smooth surfaces.
Multi-Color and Texture: PolyJet can print objects in many colors, just like a box of crayons! It can even create different textures on the surface, like rough or smooth.
Wide Range of Material Options: PolyJet uses special liquid plastics called photopolymers. These come in many varieties, including hard plastics, flexible rubbery materials, and even see-through options.
Smooth Surfaces and Minimal Finishing: PolyJet prints usually require minimal finishing because a special light instantly hardens each layer, making the surfaces smooth and accurate.
Fast Printing Speeds: PolyJet printers can print at relatively high speeds, making them suitable for rapid prototyping and small-scale production.
Applications of Multi-Color 3D Printing
Imagine a 3D printer that can not only build objects layer by layer, but also paint them in all sorts of colors at the same time!
Here are some examples you can make with a multi-color 3D printer:
Medical Models
Multi-color 3D printing enables the creation of highly realistic anatomical models, aiding in medical education, surgical planning, and patient communication.

Color-coded surgical guides can be printed to assist surgeons in complex procedures, enhancing precision and reducing operating time.
Art and Design
Multi-color 3D printing brings sculptures and figurines to life with all sorts of detail and vibrant colors, pushing the boundaries of artistic expression.

Jewelry with swirling patterns or personalized phone cases with your favorite colors – multi-color printing can bring these ideas to life.
Prototypes and End-Use Products:
Multi-color prototypes can accurately represent the final product's design, color, and texture, enabling thorough testing and refinement before mass production.
Personalized products with unique color combinations and designs can be created, catering to individual preferences and enhancing customer satisfaction.
How Multi-Color Printing Enhances Prototypes and End-Use Products
Multi-color 3D printing elevates prototypes and end-use products in several ways:
Visual Clarity and Communication: Colors can help explain different parts of a design, making it easier for people to understand and work together.
Realistic Representation: Multi-color prototypes look very realistic, so companies can test them out and make sure they look good before making a bunch of them.
Aesthetics and Branding: A splash of color can make a product more attractive and appealing to customers.
Customizable Options: With multi-color printing, you can create one-of-a-kind objects with your own special color combinations.
Conclusion
Multi-color 3D printing brings your vision to life in a spectrum of colors, whether you need high-detail prototypes for design, intricate sculptures for artistic expression, or unique personalized products.
From budget-friendly FDM options to ultra-detailed PolyJet printing, there's a multi-color printing method to fit your project and budget.
Unionfab: The Art of Multi-Color 3D Printing
We've explored the exciting world of multi-color 3D printing, and now it's your turn to bring your creations to life with Unionfab!
We offer cutting-edge technologies like PolyJet for unparalleled detail and a vast selection of FDM filaments to bring your vision to life.
Have questions or need advice? Don't hesitate to contact our expert team at Unionfab. We're here to help you navigate the world of multi-color 3D printing and turn your ideas into vibrant reality!
FAQ
Q: What are the different methods of multi-color 3D printing?
A: The two main methods are PolyJet Printing and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) with variations like single/multi-extruders and color mixing. Binder Jetting can also produce colorful parts. The main methods for multi-color 3D printing are PolyJet and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) with variations like single/multi-extruders and color mixing. Binder Jetting is another option that can produce full-color parts.
Q: Which multi-color printing method is right for me?
A: Consider factors like desired color range, detail level, material properties, budget, and project complexity. PolyJet offers exceptional detail and color accuracy but can be costlier. FDM is more affordable but may have limitations in detail and color options.
Q: What materials are available for multi-color printing?
A: FDM utilizes filaments like PLA, ABS, PETG, and TPU. PolyJet uses multi-color resins with a vast range of properties. Other methods use colored powders or binding agents.
Q: I'm having trouble achieving clean color transitions in my multi-color prints. What can I do?
A: Ensure proper filament purging in FDM printing to avoid color contamination. Consider using slicer settings like "coast at end" to minimize color bleeding. In some cases, adjusting printing temperature or retraction settings can improve color transitions.

