PLA Not Sticking to Bed: How to Prevent

Discover effective solutions for one of the most common issues in 3D printing: PLA not sticking to the bed.
Introduction
In the area of FDM 3D printing, achieving optimal adhesion between the deposited filament and the print substrate is crucial for successful print production. However, challenges often arise when utilizing polylactic acid (PLA) filament.
Understanding PLA and Bed Adhesion
What is PLA Filament

Source: all3dp.com
PLA, or Polylactic Acid, is a popular filament choice in FDM 3D printing due to its ease of use, biodegradability, and low printing temperatures.
It's a thermoplastic polymer derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane.
PLA filament comes in a variety of colors and diameters, catering to different printer needs and desired aesthetics.
What is Bed Adhesion
Bed adhesion refers to the successful bonding of the first layer of printed filament to the print bed.
This initial layer serves as the foundation for all subsequent layers, and its quality significantly impacts the final print's success.
Importance of PLA Bed Adhesion
Prevents Warping: Proper bed adhesion helps prevent warping, a common issue where the corners of the print curl upwards due to uneven cooling. This warping can ruin the entire print.
Ensures Smooth Printing: A well-adhered first layer creates a stable base for subsequent layers to be deposited on, resulting in a smoother and more consistent printing process.
Improves Overall Print Quality: Good bed adhesion translates to a cleaner bottom surface finish and overall better dimensional accuracy of the final model.
Effects of PLA Not Sticking to Bed
Failed Prints
Common Signs of Failed Prints Due to Adhesion Issues
Curling or Warping: The corners or edges of the print lift from the bed, causing the model to distort or detach completely.
Detachment: The entire print loses adhesion and lifts off the bed during the printing process, resulting in a wasted print job.
Surface Inconsistencies: The bottom layer of the print appears uneven or rough due to poor adhesion.
Frequency of Failed Prints
The frequency of failed prints due to adhesion issues can vary depending on several factors.
Severity of Adhesion Problem: The more severe the adhesion issue, the higher the chances of print failure.
Print Model Complexity: Models with large flat areas or thin features are more susceptible to warping if adhesion is poor.
Printer Settings and Calibration: Improper settings, especially bed leveling and temperature, can significantly increase the possibility of adhesion problems.
Wasted Materials
Cost Implications of Wasted Filament
Failed prints due to bed adhesion issues lead to wasted filament. The cost of wasted filament can add up quickly, especially for larger prints or projects requiring multiple attempts.
Environmental Impact
PLA is an eco-friendly filament, but wasting it contributes unnecessarily to overall material consumption.
Additionally, the energy used during a failed print run adds to the environmental footprint.
Time Loss
Impact on Project Timelines
Failed prints due to adhesion issues can significantly delay project timelines.
The time spent troubleshooting the issue, cleaning the bed, and restarting the print can be substantial.
Need for Reprinting and Adjustments
Identifying and fixing the cause of poor adhesion often involves troubleshooting, adjusting print settings, and potentially re-leveling the print bed.
This additional time investment can be frustrating, especially for time-sensitive projects.
Common Causes of PLA Not Sticking to Bed
Bed Leveling Issues
Importance of Proper Bed Leveling
The print bed needs to be perfectly level relative to the nozzle for optimal filament adhesion.
An uneven bed can cause the nozzle to be too far from the bed in some areas, resulting in poor filament squish and weak adhesion.
Conversely, if the nozzle is too close to the bed in some areas, it can scrape against the first layer and disrupt its adhesion.
How to Level the Bed Correctly
Most FDM printers have manual bed leveling procedures that involve adjusting knobs or screws underneath the bed to achieve a consistent distance between the nozzle and the bed across the entire printing surface.
There are also automated bed leveling systems on some printers that simplify this process.
Bed Temperature
Optimal Bed Temperature for PLA
A bed that's too cold won't provide enough heat to melt the first layer and promote proper adhesion.
Conversely, a bed that's too hot can cause the filament to spread excessively, reducing its ability to bond with the bed surface.
How to Adjust Bed Temperature
Most printers allow you to set the bed temperature independently from the nozzle temperature.
Experiment with different bed temperatures within the recommended range for PLA (typically around 50°C to 70°C) to find the sweet spot that optimizes adhesion for your specific filament and print settings.
Nozzle Distance
Correct Nozzle Height
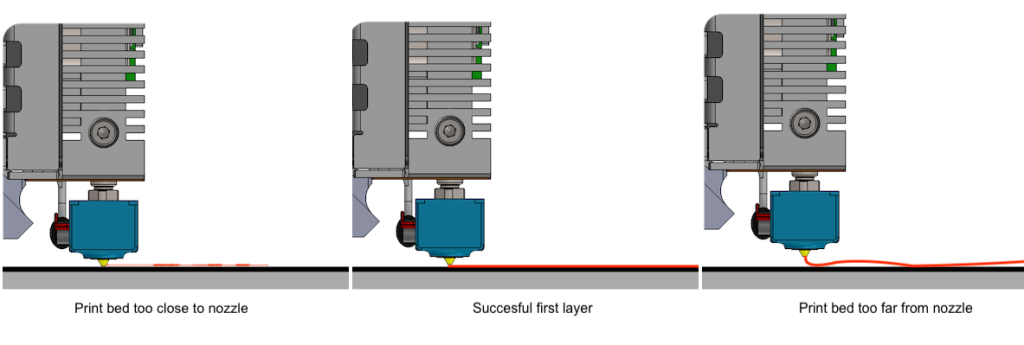
Source: support.lpfrg.com
The distance between the nozzle and the print bed, also known as the nozzle height or Z-offset, plays a vital role in bed adhesion.
If the nozzle is too far away, the filament won't be squished properly against the bed, leading to weak adhesion.
Conversely, a nozzle that's too close can scrape the filament and disrupt its bonding with the bed.
Calibrating Nozzle Distance
Many printers allow calibrating the nozzle offset through the printer's menu or by using software tools.
A thin sheet of paper test is a common method to ensure the proper nozzle height. The nozzle should just barely touch the paper when it's fed between the nozzle and the bed.
Surface Preparation
Cleaning the Bed Surface
Contaminants like dust, fingerprints, or oily residues can prevent the filament from bonding properly.
Use a suitable cleaning solution (often isopropyl alcohol) to wipe down the bed before each print.
Using Adhesion Aids
For some bed surfaces or particularly challenging prints, using adhesion aids like glue sticks or hairspray can provide an extra layer of grip to help the PLA stick initially.
However, it's important to choose the right adhesive and apply it thinly to avoid creating a messy residue or damaging the bed surface.
Avoiding PLA Not Sticking to Bed
Live Z Adjustment
How to Adjust Z-Axis During Printing
Some advanced printers offer "live Z adjustment" functionality. This allows you to fine-tune the nozzle height (Z-axis) while the printer is actually printing the first layer.
By observing how the filament lays down, you can make slight adjustments on the fly to ensure optimal squish and adhesion.
Benefits of Live Z Adjustment
Live Z adjustment provides real-time control over the nozzle distance, allowing you to ensure a perfect squish for optimal adhesion, especially for prints with uneven surfaces.
Use of Adhesion Tools
Blue Painter's Tape
Blue painter's tape is a popular and versatile bed surface for PLA printing.
It offers a good balance of adhesion and easy print removal. The slightly textured surface helps the first layer grip better.
PEI Sheets
Polyetherimide (PEI) sheets are a high-performance option for bed surfaces.
They provide excellent adhesion for a wide range of filaments, including PLA, and offer a smooth printing surface for high-quality prints.
BuildTak Sheets
Similar to PEI, BuildTak sheets are another aftermarket bed surface option specifically designed to enhance adhesion for various filaments.
These sheets are typically heat-resistant and offer a durable printing surface with good release properties.
Environmental Factors
Room Temperature
Maintaining a stable room temperature during printing can help prevent warping and curling issues that can lead to adhesion problems. Ideally, aim for a room temperature between 20°C and 25°C.
Humidity Control
Excessive humidity can negatively impact bed adhesion for some filaments, including PLA.
In very humid environments, using a filament dryer to remove moisture from the filament before printing can be beneficial.
Conclusion
Achieving optimal bed adhesion is paramount for successful PLA printing.
Understanding the interplay between bed leveling, temperature, nozzle distance, and surface preparation can help take control and prevent warping, curling, and failed prints.
Utilizing live Z adjustments, exploring alternative bed surfaces like PEI or BuildTak sheets, and maintaining a controlled printing environment can further enhance adhesion and streamline your PLA printing endeavors.
Unionfab Provides Professional 3D Printing Services
With extensive experience and a vast array of industrial-grade 3D printers, Unionfab can handle complex projects and ensure exceptional print quality for various materials beyond PLA.
At Unionfab achieve unparalleled 3D printing services and flawless products!


