ABS vs. PET 3D Printing (+ Key Comparison Chart)
Unsure between ABS and PET for 3D printing? Discover their advantages, limitations, and which material suits your design or manufacturing needs.
The Challenge: Choosing the Right Material
For many engineers, designers, and manufacturers, selecting the right material is crucial for achieving desired outcomes.
Understanding the Differences
ABS offers superior strength and heat resistance, but it requires precise environmental controls during printing. PET is easier to print and provides transparency but may not handle high temperatures as well as ABS.
Application-Specific Concerns
Have you ever wondered:
Will the material withstand high stress or heat?
Is transparency important for your project?
How do you ensure optimal results without wasting time or material?
We answer these questions in our FAQ section to help you make the right choice. Keep reading to see how ABS, PET, and PETG stack up for your project!
Unionfab Solution: We offer technical support and expertise to simplify the decision-making process.

Comparing ABS and PET
Material Properties
Property | ||
|---|---|---|
Strength | High impact resistance, durable for mechanical parts. | Good toughness, suitable for flexible parts. |
Heat Resistance | Excellent (up to 100°C), ideal for high-temperature applications. | Moderate (60-70°C). |
Printability | Challenging (requires setup) | Easy to print, beginner-friendly. |
Moisture Sensitivity | Low, stable under humid conditions. | High, must be stored properly. |
Surface Finish | Matte, can be post-processed. | Glossy, with transparent or semi-transparent options. |
Environmental Safety | Emits fumes during printing, requires ventilation. | Non-toxic, low odor, food-safe options available. |
Unionfab’s Expert Recommendations
For Engineers and Designers
ABS
Pros: High durability, heat resistance, and ideal for functional parts.
Cons: Requires a heated bed and proper ventilation due to fumes during printing.
PET
Pros: Offers a sleek finish, ease of printing, and chemical resistance.
Cons: Slightly brittle compared to ABS; may not handle high heat well.
For Small Manufacturers
ABS
Pros: Strong and reliable for tooling and industrial parts. Cost-effective for large-scale production.
Cons: Printing can be challenging due to warping and layer adhesion issues.
PET
Pros: Simplifies production with minimal warping and an attractive surface finish, perfect for consumer goods and packaging.
Cons: Limited flexibility; not as tough as other materials like ABS or PETG.
For Hobbyists
ABS
Pros: Durable and heat-resistant, excellent for long-lasting DIY projects or functional parts.
Cons: Challenging for beginners due to higher printing temperatures and need for controlled environments.
PETG
Pros: Easy to print, glossy and professional finish, excellent durability, and chemical resistance. Ideal for a wide range of personal projects.
Cons: Less rigid than ABS, making it unsuitable for parts requiring extreme hardness or high-temperature resistance.
Common Applications for ABS and PETG
ABS Applications
Automotive Components: Durable and heat-resistant parts like dashboards, brackets, and handles.
Toolig and Prototypes: Strong functional prototypes, jigs, and fixtures for industrial use.
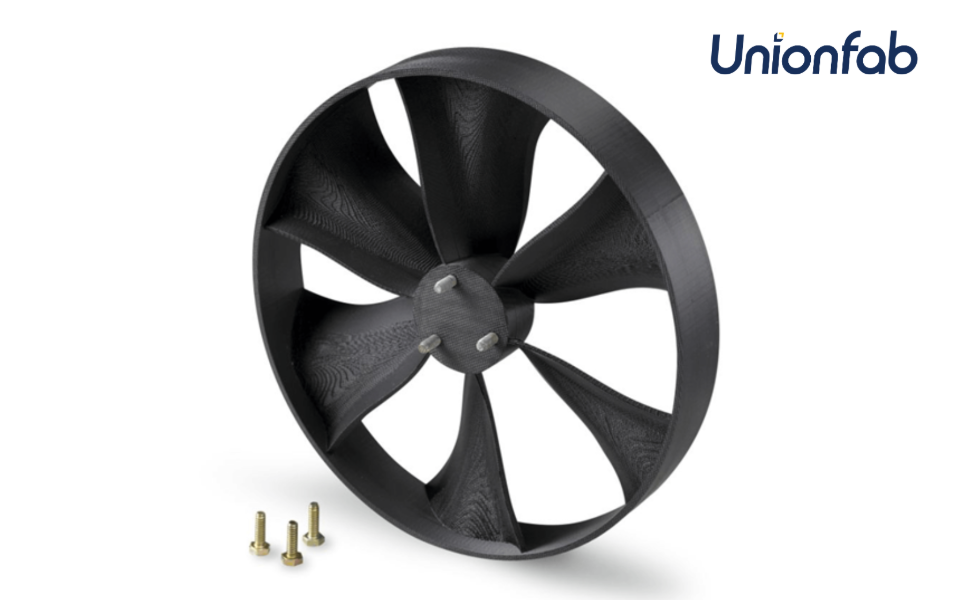

Source: Unionfab
PET Applications
Consumer Packaging: Transparent and durable trays, containers, and protective covers.
Medical and Food-Safe Products: Items like sample holders, food containers, and non-critical medical devices.
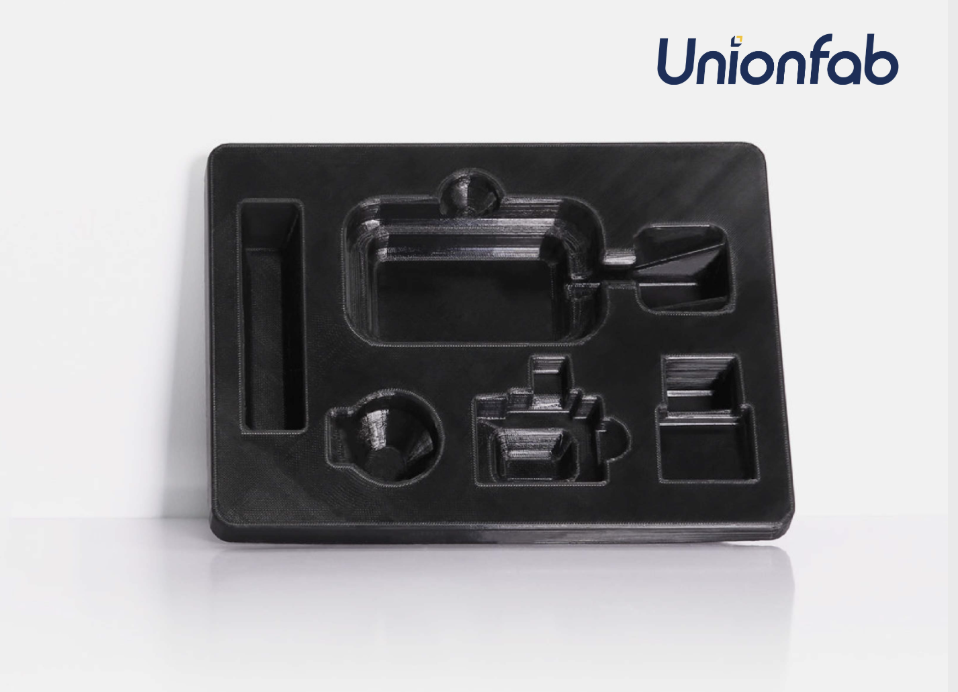

Source: Unionfab
Advantages of ABS and PET
ABS Advantages
Durability and Strength: ABS is known for its toughness and impact resistance, making it ideal for functional prototypes, enclosures, and parts subjected to mechanical stress.
Heat Resistance: Its higher glass transition temperature (~105°C) allows it to perform better in high-temperature environments compared to many other common 3D printing plastics.
Good Machinability: ABS can be easily sanded, drilled, and post-processed for smoother finishes or assembly.
Cost-Effective: Widely available and affordable, ABS is a popular choice for general-purpose and industrial applications.
Acetone Smoothing: ABS can be chemically smoothed using acetone, creating a glossy and professional finish while strengthening the part's surface.
Recyclability: While not as eco-friendly as some alternatives, ABS can be recycled, reducing its environmental footprint when managed properly.
PET Advantages
Strength and Flexibility: PET offers excellent strength and moderate flexibility, making it suitable for parts requiring toughness and slight elasticity.
Chemical Resistance: Resistant to water, alcohols, and a variety of chemicals, PET is ideal for applications requiring exposure to liquids or harsh environments.
Food Safety: Certain grades of PET (e.g., PETG) are FDA-approved for food contact, making them suitable for food-safe applications.
Low Warping: PET is less prone to warping compared to ABS, resulting in better dimensional accuracy and easier printing for large parts.
Transparency: PET can be printed in transparent or translucent colors, making it a great choice for aesthetic projects or parts requiring visibility.
Environmental Impact: PET is recyclable and can be made from recycled plastics (like PET bottles), contributing to a circular economy.
Tips for ABS and PET 3D Printing
Tips for ABS Printing:
Enclosed Printing Environment: Use a 3D printer with an enclosed chamber to prevent warping and cracking caused by temperature fluctuations.
Bed Adhesion: Apply a suitable adhesive like ABS slurry or Kapton tape to the print bed to ensure proper adhesion.
Ventilation: ABS emits fumes during printing, so work in a well-ventilated area or use an air filter to maintain safety.
Post-Processing: To achieve a smooth finish, consider acetone vapor smoothing for polishing ABS prints.
Tips for PET Printing:
Temperature Control: Set the nozzle temperature between 220°C and 250°C for optimal extrusion, and maintain the bed temperature around 70°C-90°C to avoid warping.
Stringing Prevention: Fine-tune retraction settings to minimize stringing, a common issue with PETG.
Avoid Overheating: Excessive heat can cause PET prints to become overly soft and lose detail, so adjust settings carefully.
Storage: PET is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air. Store it in a dry box or airtight container to maintain print quality.

PETG – What Makes It Different From PET?
At Unionfab, while we don't currently offer PET 3D printing, we do specialize in PETG printing. PETG is PET with added glycol, which enhances its durability, flexibility, and ease of use in 3D printing.
Why Choose PETG?
Toughness with Flexibility PETG combines the strength of PET with added flexibility, making it perfect for durable parts that can withstand stress without breaking.
Chemical and Water Resistance PETG shares PET’s resistance to water, alcohols, and a range of chemicals, ensuring its performance in harsh environments.
Ease of Printing PETG’s reduced tendency to warp or shrink during printing results in high dimensional accuracy and excellent layer adhesion, even for large or intricate designs.
Food Safety Like PET, PETG is food-safe (when printed under appropriate conditions), making it suitable for kitchen tools, containers, and other food-related applications.
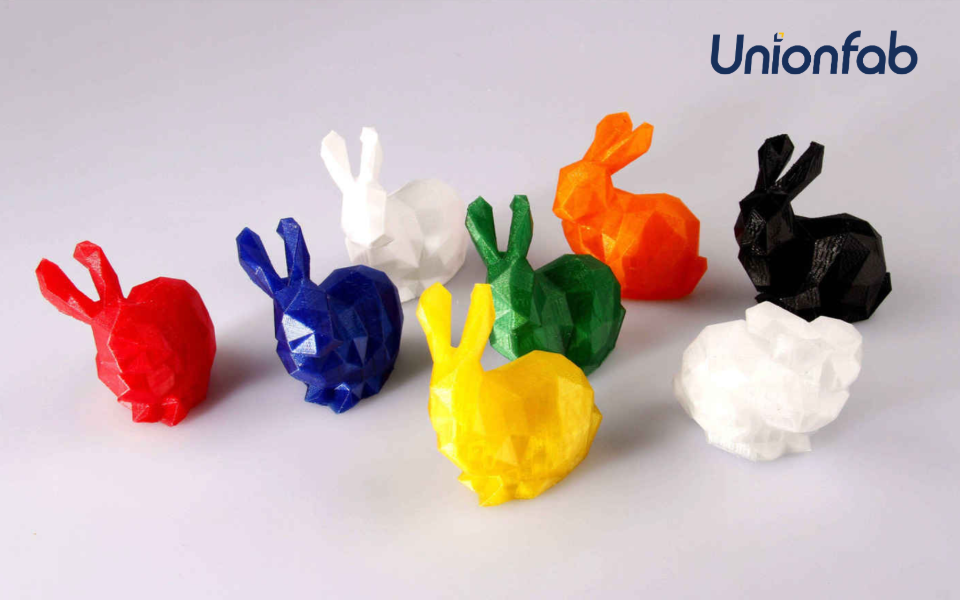

Source: Unionfab
Applications of PETG
Thanks to its versatility, PETG is ideal for:
Protective housings and enclosures: Durable and resilient against impact.
Medical and food-safe parts: Compliant with food safety regulations when printed correctly.
Outdoor components: Excellent chemical and UV resistance for outdoor use.
Functional prototypes: Tough and flexible for iterative design.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways
ABS, PET, and PETG are versatile and valuable materials in 3D printing, each excelling in different applications:
ABS is ideal for projects requiring high strength, heat resistance, and durability, making it a popular choice for automotive parts and industrial tooling.
PET stands out for its ease of printing, glossy finish, and food-safe properties, making it perfect for consumer packaging and medical applications.
PETG combines the strengths of PET with enhanced toughness, flexibility, and chemical resistance. Its ease of printing, transparency, and durability make it suitable for functional prototypes, protective housings, food-safe tools, and outdoor components.
Let Unionfab Support Your Next 3D Printing Project
Make your material choice with confidence:
Contact Unionfab for Expert Advice: Our team is ready to provide tailored recommendations for your project.
Explore Unionfab’s Material Library: Discover in-depth guides, technical insights, and examples of ABS and PET applications.
At Unionfab, we’re committed to delivering professional-grade results and helping you unlock the full potential of 3D printing materials. Get started today!

FAQs: ABS vs. PET in 3D Printing
Addressing the Key Questions
1. Will the material withstand high stress or extreme heat?
ABS is the best choice for projects that require high strength and heat resistance. Its high glass transition temperature (~105°C) allows it to perform well in applications exposed to heat or mechanical stress, such as automotive parts and industrial tooling.
PETG, while not as heat-resistant as ABS, still offers good mechanical properties, making it suitable for functional prototypes and parts that need to withstand moderate stress without deforming or cracking.
PET, while offering some strength, is more prone to deformation under heat, making it less ideal for parts exposed to extreme temperatures.
2. Is transparency important for your Project?
PETG is the go-to choice if transparency is a key factor in your design. It’s naturally clear, offering excellent visual clarity for prototypes where appearance matters—such as protective covers, cosmetic products, or display items. It’s also available in various colors if you need some vibrant hues while maintaining transparency.
PET also offers clear printing options but might be slightly more difficult to work with compared to PETG, which provides a smoother, more polished finish.
ABS is generally not transparent and can have a matte finish, making it unsuitable for applications that require visual clarity or a polished appearance.
3. How do you ensure optimal results without wasting time or material?
PETG is easy to print, offering consistent results and minimal waste.
ABS requires more care to avoid warping and can be harder to manage.
PET is easy to print but lacks the strength for more demanding applications.
For more tips on optimizing your printing results, check out the tips above.
People Also Ask
1. Which is stronger, ABS or PET?
Both materials offer high strength, but ABS generally has higher impact resistance, making it suitable for mechanical parts. PET provides good toughness and flexibility, ideal for items requiring some pliability.
2. Is PET safer than ABS?
Yes, PET is considered safer for 3D printing as it emits fewer fumes during printing compared to ABS. Additionally, PET is often food-safe, whereas ABS is not recommended for food-contact items.
3. Does PET warp like ABS?
PET has better dimensional stability and is less prone to warping compared to ABS. This makes PET easier to print without requiring an enclosed printer or heated bed, though a heated bed can improve adhesion.
4. Can I use PET for outdoor applications?
Yes, PET has good UV and weather resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications. In contrast, ABS can degrade over time when exposed to UV light unless properly treated or coated.
5. Is ABS or PET easier to print with?
PET is generally easier to print with due to its lower tendency to warp and minimal odor during printing. ABS requires more precise temperature control and ventilation, making it more challenging for beginners.

