CNC Machining Price Guide: Breakdown & Price Comparison

Break down CNC machining prices, learn cost-saving strategies, and compare several major CNC service providers.
Introduction
CNC machining plays a critical role in modern manufacturing, offering high precision, reliability, and flexibility across a wide range of industries. However, the cost of CNC machining can vary significantly depending on factors such as part geometry, material selection, machining strategy, tolerance requirements, and production volume.
This guide is designed to help you understand what drives CNC machining costs and how to manage them effectively. In the sections below, we’ll break down the cost structure of CNC machining, explore practical ways to reduce machining costs, and compare pricing among major CNC machining service providers.
By the end, you’ll have the insights needed to estimate costs more accurately and make informed decisions for your project.
What Is CNC Machining?
CNC Machining (Computer Numerical Control Machining) is a subtractive manufacturing process in which computer-controlled machines remove material from a solid block to produce precise, functional parts. Using digital design files (CAD/CAM), CNC machines such as mills, lathes, and routers cut materials like aluminum, steel, plastics, and titanium with high accuracy and repeatability.
CNC machining is widely used across industries including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, electronics, and industrial equipment. It is especially suitable for projects that require tight tolerances, consistent quality, and real-world performance, whether for prototypes or end-use parts.
CNC Machining Cost Breakdown
Understanding where these costs come from—and how they change with design and production decisions—is essential for accurate budgeting and supplier selection. Below, we break down the main cost components involved in CNC machining.
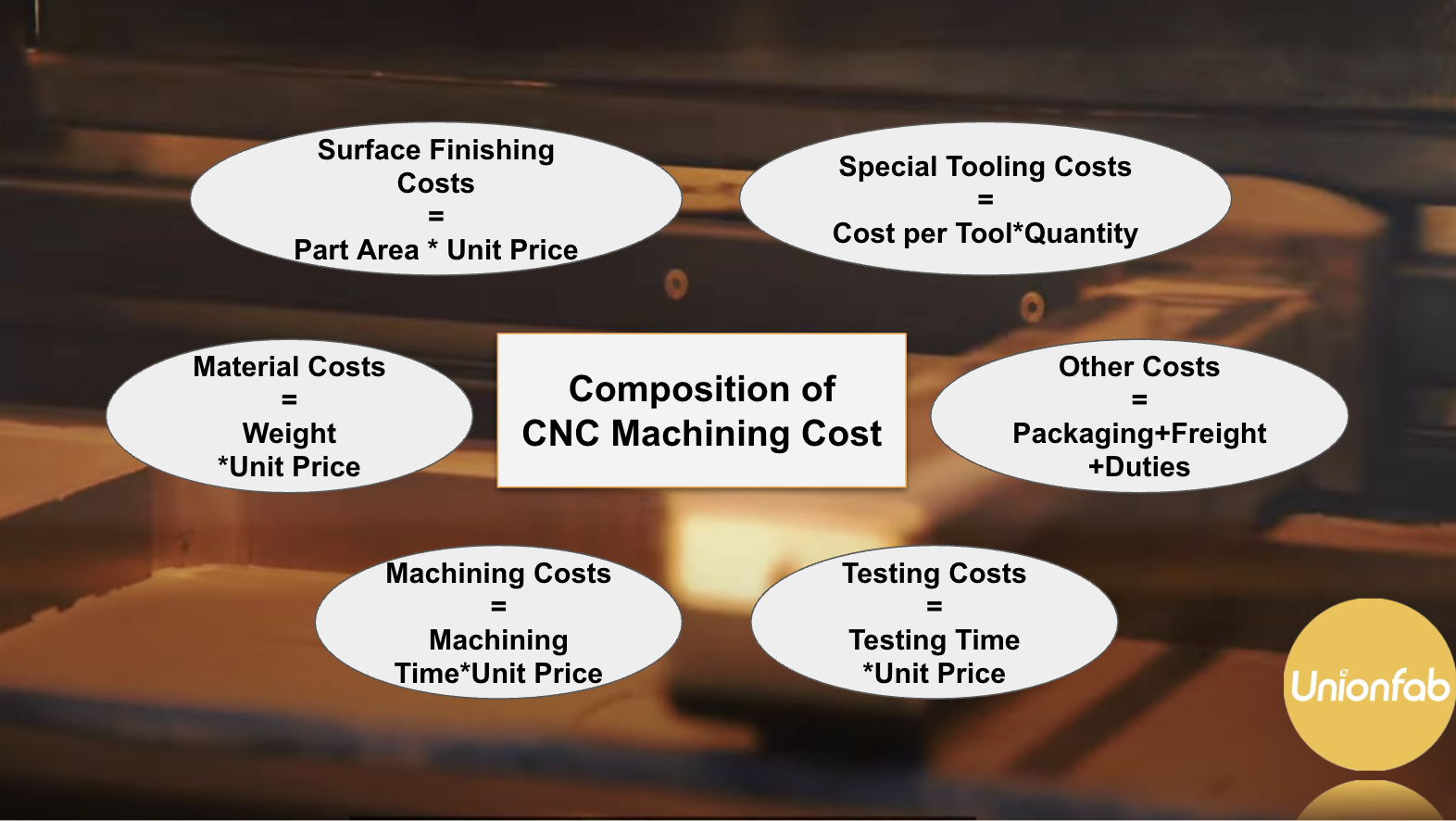
Material Cost
Material cost typically represents a significant portion of the total machining cost. The choice of material affects both raw-material expense and the complexity of the machining process.
Raw Material: The cost of the raw material used in CNC machining, such as metal, plastic, or composite, can vary widely depending on the type, grade, size, and quality required.
Waste Material: CNC machining is a subtractive process, meaning excess material is removed to form the desired part. This waste factor must be considered, especially for expensive materials.
Price of Common CNC Materials
Materials used in CNC machining vary widely and can include metals (such as aluminum, steel, and titanium), plastics, ceramics, and composite materials.
To help illustrate how material selection affects overall machining cost, below is a simplified price-tier table showing the relative cost levels of common CNC materials for reference.
The price tiers below provide an approximate comparison, where $ indicates low cost and $$$$$ indicates very high cost.
Category | Material | Price Tier |
|---|---|---|
Metals | Aluminum | $ |
Copper | $$$ | |
Brass | $$$ | |
Bronze | $$$ | |
Steel | $$$ | |
Stainless Steel | $$$ | |
Magnesium | $$$$$ | |
Titanium | $$$$$ | |
Plastics | PC (Polycarbonate) | $$$ |
ABS | $$$ | |
PEEK | $$$$$ | |
PMMA (Acrylic) | $ | |
POM | $$ | |
PTFE (Teflon) | $$ | |
PA (Nylon) | $$ | |
Composites | FR4 (Epoxy Fiberglass) | $$ |
Synthetic stone (CDM) | $$ | |
Bakelite PF | $$ | |
Graphite | $$ | |
Ceramics | Silicon Nitride (Si3N4) | $$$$$ |
Alumina (Al2O3) | $$$$$ | |
Zirconia (ZrO₂) | $$$$$ |
Machining Cost
Machining cost refers to the expenses incurred during the actual production of parts on the CNC machine. This cost is influenced by several factors, including the complexity of the part design, the type of CNC machine used, and the time required to complete the machining process.
Machining Time: CNC machines operate at an hourly rate. Parts with intricate geometries or high precision require more machining time, which increases costs.
Machine Type and Capability: Advanced CNC machines with higher capabilities (such as multi-axis machines) typically cost more to operate than basic 3-axis machines. These machines may also require skilled operators, contributing to the overall cost. The following is a reference price.
CNC Type | Rate |
|---|---|
3-axis | $40/hr |
4-axis | $45-50/hr |
5-axis | $75-120/hr |
Special Tooling Cost
Special tooling costs refer to any custom or non-standard tools required for the CNC machining process. These tools are often needed for specialized operations or to accommodate unique design features that cannot be handled with standard tooling. If a specific part requires custom or specialized tools, such as custom cutters, fixtures, or jigs, the costs of creating and maintaining these tools can add up.
Heat Treatment Cost
Heat treatment is an important step in CNC machining—especially for metal parts—to improve material properties such as hardness, tensile strength, toughness, and resistance to wear or corrosion. Below is an estimated cost reference for different heat-treatment processes:
Heat Treatment Process | Estimated Cost (USD per part) |
|---|---|
Annealing | $0.5 – $3 |
Hardening and Tempering | $5 – $25 |
Case Hardening | $10 – $50 |
Stress Relieving | $1 – $5 |
Titanium Heat Treatment | $100 – $200 |
Surface Finishing Cost
Surface finishing is the final stage in CNC machining, where the part's surface is refined to meet specific aesthetic or functional requirements. The cost varies depending on whether the finish involves simple deburring or more complex coating and treatment. Below is an estimated cost reference for common finishing processes:
Surface Finish Process | Estimated Cost (USD per part) |
|---|---|
Polishing | $2 – $15 |
Anodizing | $3 – $12 |
Painting or Coating | $5 – $20 |
Electroplating (Nickel/Chrome) | $10 – $30 |
Sandblasting / Media Blasting | $2 – $10 |
Passivation | $3 – $8 |
Laser Etching / Engraving | $5 – $20 |
Testing Cost
Testing ensures that the CNC machined parts meet the required specifications and performance standards. Depending on the part’s function and industry requirements, testing can be extensive or minimal, influencing the overall cost.
Other Costs
Packaging Fees Packaging fees may also be added to the final cost, especially for fragile or complex parts that require special care during transportation.
Standard Packaging (Free)
The most common packaging is the corrugated box with bubble wrap or foam paddings inside.
Protective Packaging (Paid)
Depending on the final product, additional protective packaging such as wooden crates or even custom-made flight cases may be required.
Here's a general breakdown of costs:
Wooden Crates:
* Simple wooden crates for small to medium-sized parts typically range from $50 to $300.
* For larger or more complex parts, prices can go up to $500 or more, depending on the wood type, size, and level of reinforcement needed.
Custom-Made Flight Cases:
* Basic custom flight cases can cost around $200 to $500 for small items.
* For larger, fully customized cases with specialized padding and materials, prices can range from $800 to $2,000 or more.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees are another important consideration when calculating the total cnc cost, especially for cross-border orders. Different carriers (e.g., USPS, FedEx, DHL) offer varying rates depending on the destination, size, weight, and urgency of delivery.
Customs Duties
When shipping cnc parts internationally, customs duties may apply, depending on the destination country’s import regulations. Customs duties can vary widely, but typically range between 5% to 20% of the total product value, depending on the country’s specific tariff regulations.
Curious about the cost for your specific project? Upload your CAD files to our cost calculator and get an instant CNC machining quote tailored to your parts.
How to Reduce CNC Machining Costs
CNC machining offers precision and flexibility, but costs can add up quickly if design, materials, and production decisions aren’t optimized. The good news is that many cost drivers are within your control. By making informed choices early in the design and manufacturing process, you can significantly reduce expenses without sacrificing quality.
Below are the most effective strategies to lower CNC machining costs.
Design Optimization
Simplify part geometry: Minimize sharp internal corners, deep pockets, and intricate features that increase machining time.
Use standard tool sizes: Designing features compatible with commonly available end mills, drills, and cutters reduces setup and tool costs.
Consolidate multiple parts: Combine parts where possible to save on assembly, tooling, and machine setups.
Optimize wall thickness: Avoid very thin walls that are difficult to machine; slightly thicker walls increase stability and reduce rejects.
Plan for single or fewer setups: Reduce the number of machine repositionings to cut labor and runtime costs.
Reinforce small features: Use ribs or thicker walls to maintain stiffness and avoid machining difficulties.
Material Selection Tips
Choose cost-effective materials: Select materials that meet functional requirements without over-specifying (e.g., aluminum instead of titanium when high strength is not critical).
Consider machinability: Softer or easier-to-machine materials reduce tool wear, machine time, and labor.
Reduce waste: Using standard material sizes and readily available stock minimizes extra cutting and preparation.
Lightweight materials for handling: Lighter materials (plastics, aluminum) reduce handling difficulty and shipping costs.
Balance properties with cost: Only use high-performance or exotic materials when the application truly demands them.
Tolerance Control Strategies
Apply tight tolerances only where necessary: Critical dimensions need high precision, but non-critical areas can use standard tolerances.
Relax non-essential tolerances: This reduces machining time, tool wear, and inspection requirements.
Use standard tolerance ranges: Aligning tolerances with typical machine capabilities avoids expensive secondary operations.
Communicate critical tolerances clearly: Clear drawings help the manufacturer prioritize precision where it matters.
Avoid over-engineering: Excessive precision can significantly increase cost without adding real value.
Surface Finish Considerations
Specify functional finishes: Only request polished or ultra-smooth surfaces where necessary for function or aesthetics.
Avoid unnecessary finishing: Rougher finishes are cheaper and faster to produce.
Leverage machine capabilities: Choose cutting methods that produce the required finish directly without secondary operations.
Communicate finish expectations: Ensure the manufacturer knows which areas need higher quality and which can be left standard.
Combine finishing steps: Minimize separate finishing processes like grinding or polishing whenever possible.
Batch Size and Production Volume Optimization
Leverage economies of scale: Larger batches reduce the per-part cost by spreading setup and tooling costs over more units.
Plan optimal order quantities: Slight increases in batch size can achieve significant savings without overproduction.
Nest multiple parts per setup: Machining multiple components in a single run reduces machine time per unit.
Align production with storage and deadlines: Balance batch size with available space and project timeline.
Consider repeat orders: If the part will be produced again, slightly larger initial batches can save future setup costs.
The cost of CNC machining generally decreases with an increase in quantity due to the principle of economies of scale.
To present it more clearly, we have created a comparison chart with 3D printing and casting, showing the relationship between processing quantity and price for all three methods.
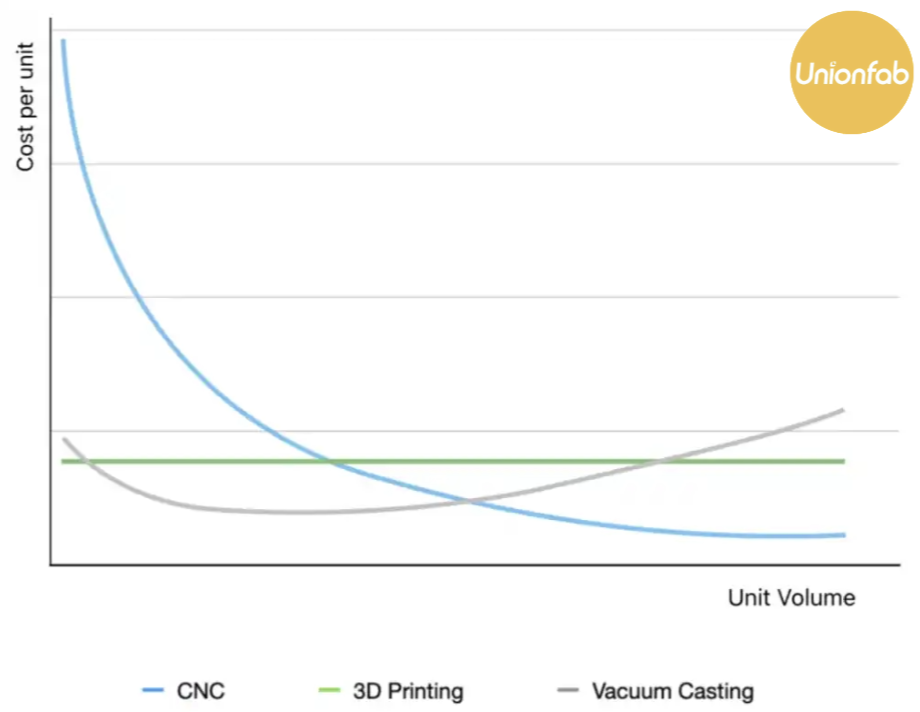
If you want to know more differences between these 3 manufacturing methods, you can read this article: 3D Printing vs. CNC vs. Vacuum Casting: the Ultimate Comparison.
Summary
By focusing on smart design, material selection, tolerances, surface finishes, and production planning, you can substantially reduce CNC machining costs. Early collaboration with your manufacturer ensures cost-effective production, efficient workflows, and high-quality parts, giving you the best value for your investment.
CNC Machining Service Provider Comparison
When comparing CNC machining service providers, it’s important to evaluate several key factors—such as manufacturing capabilities, supported materials, online quoting systems, lead times, and overall pricing.
The table below summarizes how several major providers perform across these factors, giving you a clear overview before reviewing the cost comparison for a specific part.
Service Provider | One-line Profile | CNC Solutions | Supported Materials | Online Instant Quoting System |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Xometry | A US-based, factory-less global manufacturing service provider | CNC milling, CNC turning, CNC routing, High-volume CNC machining | Metals: Aluminum, Copper, Bronze, Brass, Stainless steel, Steel, Titanium, Zinc; Plastics: HDPE, Acetal (Delrin), Polypropylene, UHMW-PE, Nylon 6/6, Acrylic, ABS, Polycarbonate, PEEK, PTFE-Teflon, Garolite, PVC, ULTEM | ✅ |
Protolabs Network (formerly Hubs) | A Europe- and US-based, factory-less global manufacturing service provider | CNC milling, CNC turning | Metals: Aluminum, Stainless steel, Mild steel, Brass, Copper, Alloy steel, Tool steel, Titanium, Inconel, Invar 36; Plastics: POM (Delrin/Acetal), Nylon, PPSU, ABS, PEEK, PTFE (Teflon), Polycarbonate, Polyethylene, PVC, PMMA (Acrylic), PET, Polypropylene, G-10, FR4, PEI | ✅ |
Fictiv | A US-based, factory-less global manufacturing service provider | CNC milling, CNC turning, Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), Gear hobbing, High-volume CNC machining, Large CNC parts | Metals: Aluminum, Stainless steel, Steel, Titanium, Copper, Brass, Bronze, Cast Iron, Magnesium, Invar, Kovar, Tool Steel, A2 Tool Steel, Zinc; Plastics: ABS, Acrylic, Nylon, Polycarbonate, PEEK, PPS, PTFE, PVC, Torlon, UHMW, Ultem, Polypropylene, HDPE, Delrin; Composites: Garolite G-10 | ✅ |
Unionfab | A China-based global manufacturing service provider with in-house production facilities | CNC milling, CNC turning, CNC routing, CNC drilling, CNC grinding, Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), Wire EDM, Multi-axis CNC | Metals: Steel, Stainless steel, Aluminum, Titanium, Copper; Plastics: ABS, PC, PE, POM, PMMA, PP, PU, PVC, PA6/PA66, PTFE, PEEK, ESD 225 POM Acetal, MC501CD R6; Composites: Synthetic stone (CDM), Bakelite PF, FR4 Epoxy Fiberglass, Zirconia (ZrO₂) | ✅ |
*Disclaimer: The information presented above was collected from the official websites of each CNC machining service provider on December 5, 2025. This comparison is provided for reference purposes only.
Cost Comparison Based on the Same CNC Machined Part
To provide a practical perspective on how these differences affect actual project costs, we conducted a cost comparison using the same 3D model across several CNC machining providers. All other parameters were kept consistent to ensure a fair evaluation.
The specifications of the part and the resulting price and lead time comparisons are summarized below.
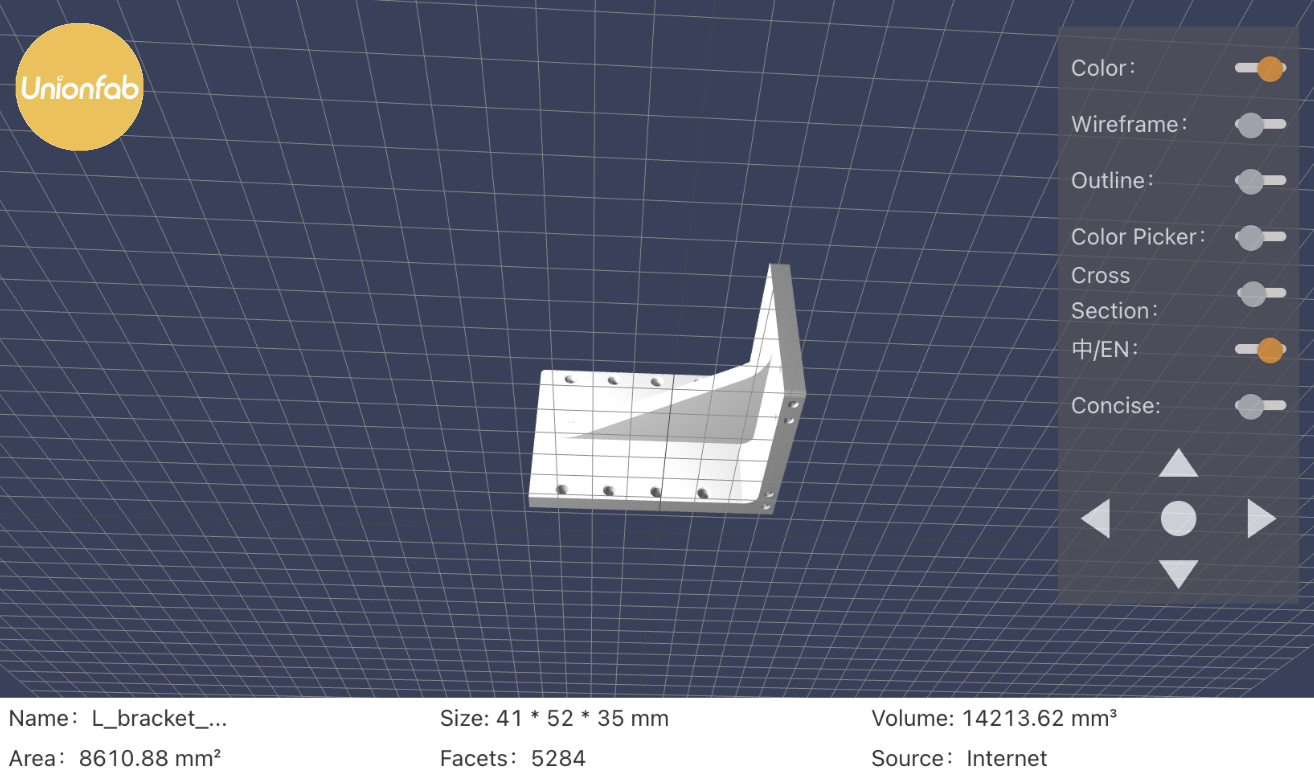
Model Specifications:
● Dimensions: 41 × 52 × 35 mm
● Process: CNC
● Material: Aluminum 6061-T6
● Quantity: 500 units
● Roughness: As machined (Ra 3.2μm)
● Part markings: No
Price and Lead Time Comparison
Service Provider | Lead Time (Business Day) | Unit price (USD) | Total Price (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Xometry | 8 | 37.51 | 18,755 | Production Location: Made in USA |
13 | 19.69 | 9,845 | Production Location: Made in USA | |
17 | 5.55 | 2,775 | Production Location: Made Internationally | |
20 | 14.24 | 7,120 | Production Location: Made in USA | |
Protolabs Network (formerly Hubs) | 18 | 9.61 | 4,805 | Shipping: 3-5 business days ($0) |
23 | 9.01 | 4,505 | Shipping: 3-5 business days ($0) | |
30 | 8.50 | 4,250 | Shipping: 3-5 business days ($0) | |
Fictiv | 8 | 28.17 | 14,085 | Production Location: USA & Mexico |
11 | 23.99 | 11,995 | Production Location: USA & Mexico | |
15 | 23.08 | 11,540 | Production Location: USA & Mexico | |
8 | 12.94 | 6,470 | Production Location: Overseas | |
12 | 9.42 | 4,710 | Production Location: Overseas | |
17 | 8.72 | 4,360 | Production Location: Overseas | |
Unionfab | 12 | 6.62 | 3,310.34 | Manually verified actual machining price |
*Notes: Prices for Xometry, Protolabs Network, and Fictiv were collected from their official websites’ automated quoting systems on December 5, 2025, and may differ from actual quotes. These figures are for reference only.
The presence of multiple rows for a single provider indicates that they offer several lead-time and pricing options for the same order. Additionally, Unionfab’s price has been manually verified and reflects the actual machining cost for this specific model.
Why Choose Unionfab for CNC Machining
Unionfab combines advanced equipment, diverse materials, and rigorous quality standards to provide reliable CNC machining services for a wide range of applications. Whether you need prototypes, low-volume production, or end-use parts, our team ensures precision, speed, and consistency.
Certifications
Our operations are supported by ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, and AS 9100D certified quality management systems, ensuring that every component meets your exact specifications.
Materials and Equipment
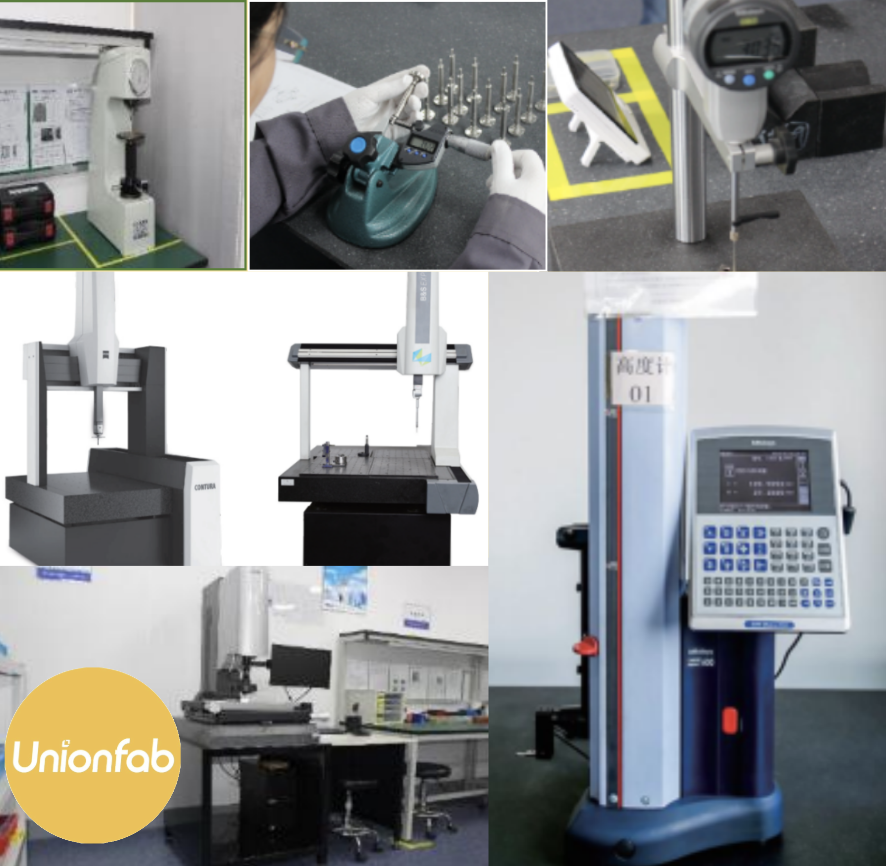
Unionfab provides a wide range of materials for CNC machining, covering metals, plastics, and composites to suit diverse project needs. Our equipment, including 50+ production machines with 3-, 4-, and 5-axis capabilities, supports these materials across our strategically located facilities. Our capabilities are complemented by multiple high-precision testing devices, ensuring every part meets stringent quality and accuracy standards.
50+ Production Equipment

10+ Testing Equipment

Post-processing Available
Post-processing | Effect |
|---|---|
Anodizing |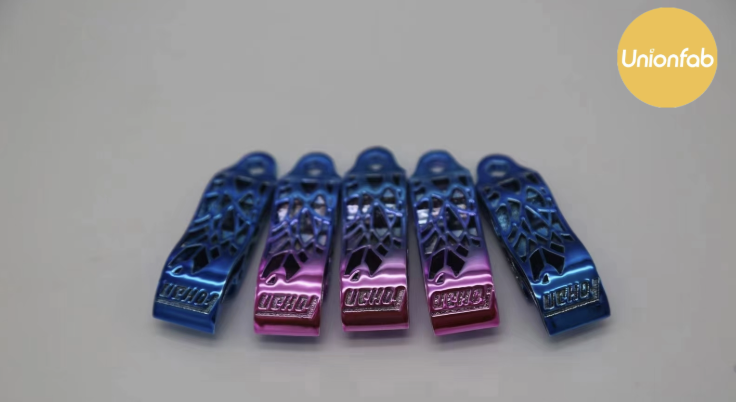 
|
Electroplating |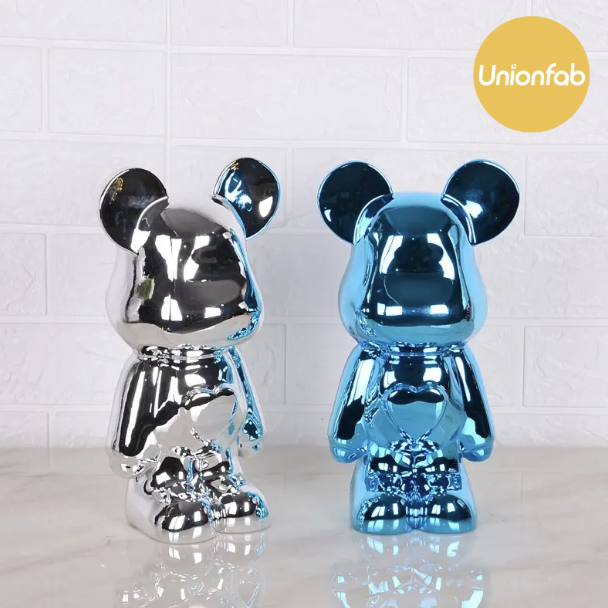 
|
Screen Printing | 
|
Galvanizing | 
|
Painting | 
|
Blackening/Black Oxide Treatment | 
|
Sandblasting |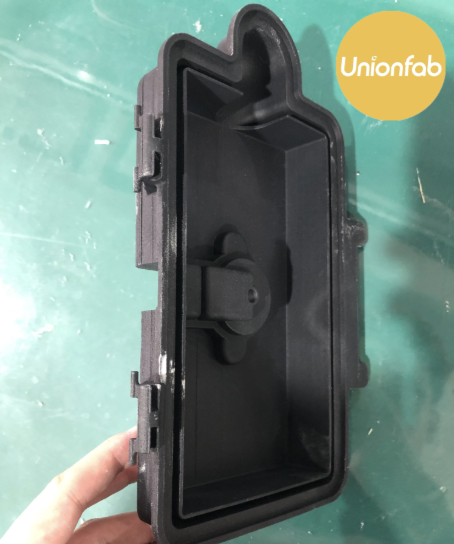 
|
Polishing | 
|
Passivation | 
|
Lead Time
Aim: 100% On-Time Delivery, ≥98% Shipment Quality, 100% Customer Satisfaction
Lead Time: 7 -15 days
New to Unionfab?
Enjoy 10% off your first CNC machining order when you sign up today!
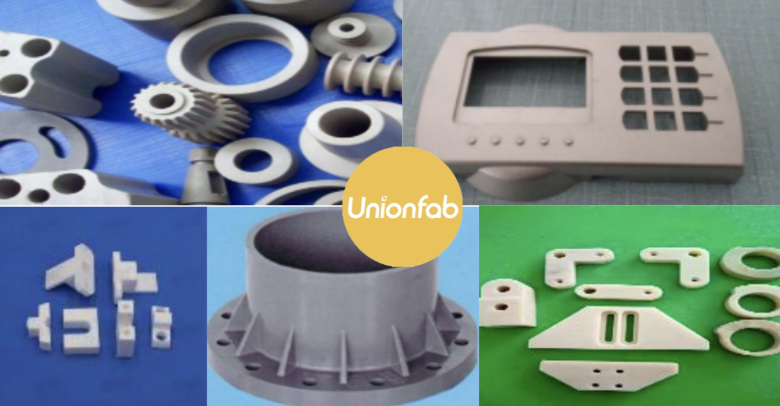
Product Examples
Below are examples of parts Unionfab has successfully machined across various industries, showcasing our expertise with a wide range of materials: aluminum alloys, steel and alloy steels, stainless steels, titanium alloys, brass and copper, as well as engineering plastics like PC, PVC, PEEK, PTFE, PA, and acrylics.







