A Guide to Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Materials [+ Free Datasheets]

Explore our ultimate guide to SLS materials, including PA12, PA11, and glass fiber-filled options. Compare key properties and download free resources for better 3D printing results!
Introduction
Selecting the right material is crucial for achieving the desired performance in 3D printing. In the case of SLS (Selective Laser Sintering), material choice directly impacts durability, flexibility, heat resistance, and more. With a wide range of options available, how do you ensure the perfect fit for your application?
This guide breaks down the essential considerations for choosing SLS materials and highlights their applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Along the way, we’ll connect you to key resources—including detailed material specifications and expert advice—to help you make informed decisions and achieve optimal results.
What is SLS 3D Printing?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a type of 3D printing technology that uses a high-powered laser to fuse powdered material, layer by layer, into a solid object.
It lets you make complex shapes, use diverse (mostly plastic) materials, create strong and durable parts, need little finishing work, and produce multiple parts at once.

How SLS 3D Printing Works
1. Preparation
Design: A 3D model is created using CAD software, sliced into layers, and prepared for printing.
Material Loading: The build chamber is filled with a fine powdered material, such as Nylon 12 or TPU. The quality of this powder — its particle size, shape, and flowability — directly impacts the uniformity of each layer and the final print accuracy.
2. Preheating
The build chamber is heated to just below the material's melting point. This reduces the laser energy required for sintering while minimizing the risk of thermal distortion.
For example, Nylon 12's low melting point ensures efficient energy use and strong layer bonding.
3. Layer-by-Layer Fusion
Laser Scanning: A CO2 laser scans and selectively fuses the material in each layer based on the object’s cross-section. The material's type and properties play a crucial role here.
Nylon 11 and 12 provide mechanical strength and flexibility, making them ideal for functional parts.
Composites with fillers (e.g., carbon or glass fibers) enhance stiffness and thermal resistance, catering to specialized applications.
Powder Spreading: After fusing a layer, a recoater spreads a new layer of powder.
4. Cooling
The entire build cools slowly within the chamber to prevent warping or thermal stress.
5. Post-Processing
Once the print is complete, un-sintered powder is removed, and the part undergoes post-processing steps like cleaning, bead blasting, or dyeing.
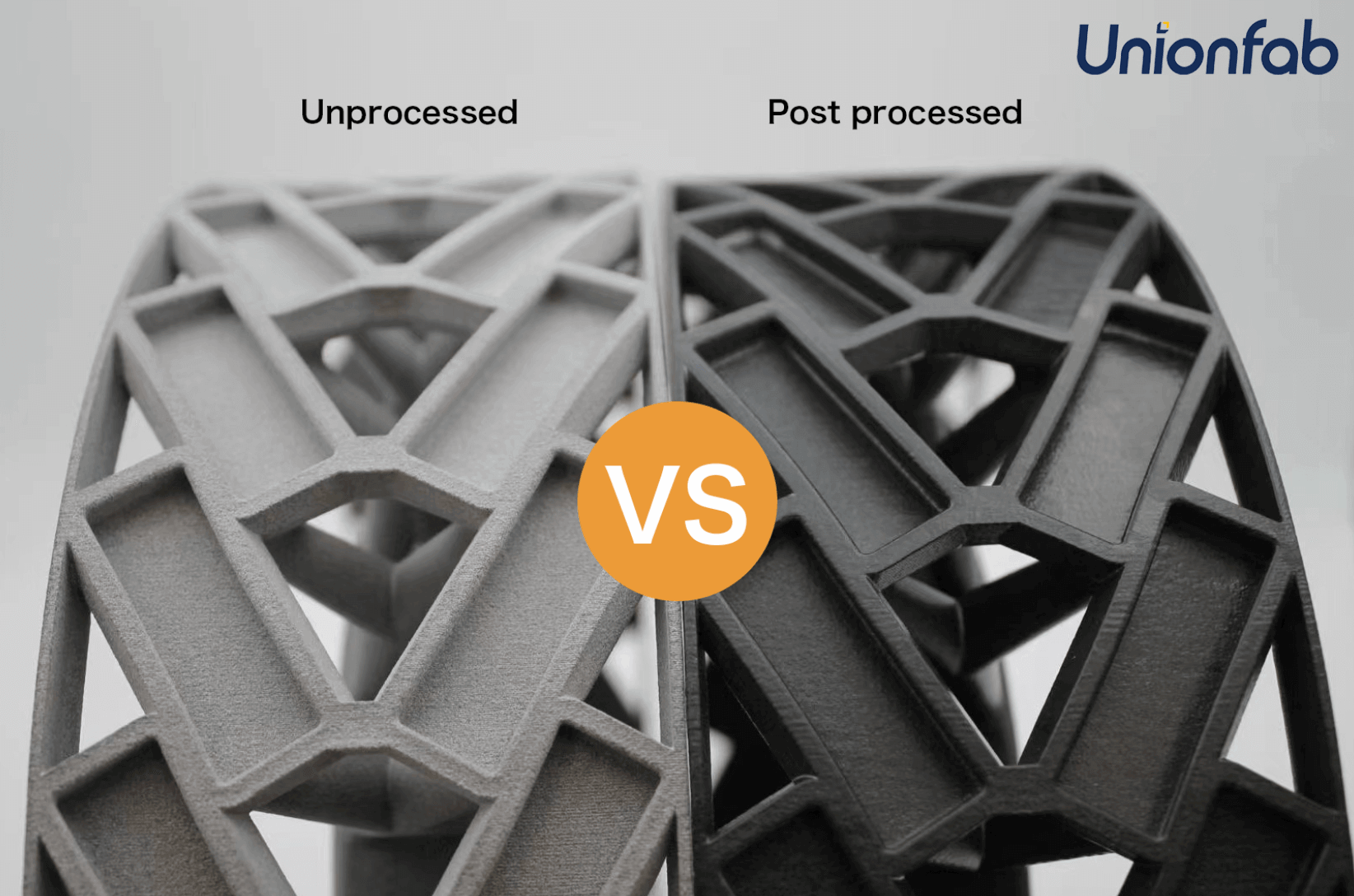
The unused powder, depending on its quality and degradation during the process, can often be recycled and mixed with fresh powder for subsequent builds.

Types of SLS Materials
In Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), a wide variety of materials can be used depending on the desired application and properties. Below is a comparative overview of some of the most commonly used SLS materials.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
TPU is your go-to material for applications requiring flexibility and impact resistance. Its ability to endure repeated stress makes it ideal for creating soft yet durable components such as medical devices, wearable products, and protective casings.
When designing with TPU, remember to account for its slightly lower tensile strength compared to rigid plastics, and leverage its elasticity for dynamic parts.

Nylon 12 (PA 12)
As the most versatile nylon variant, Nylon 12 strikes a balance between printability, strength, and durability, making it an excellent choice for functional prototypes and consumer goods. Its dimensional stability also ensures consistency across multiple iterations.

Nylon 11 (PA 11)
Nylon 11 is similar to Nylon 12 but with better chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption. It’s a flexible and durable material used for parts that need to withstand impact and stress, like automotive or medical components.

Nylon 6 (PA 6)
Nylon 6 is stronger and more heat-resistant than other nylons. While it’s more rigid, it’s ideal for parts that need to bear heavy loads or resist wear, such as gears, bearings, and mechanical parts.
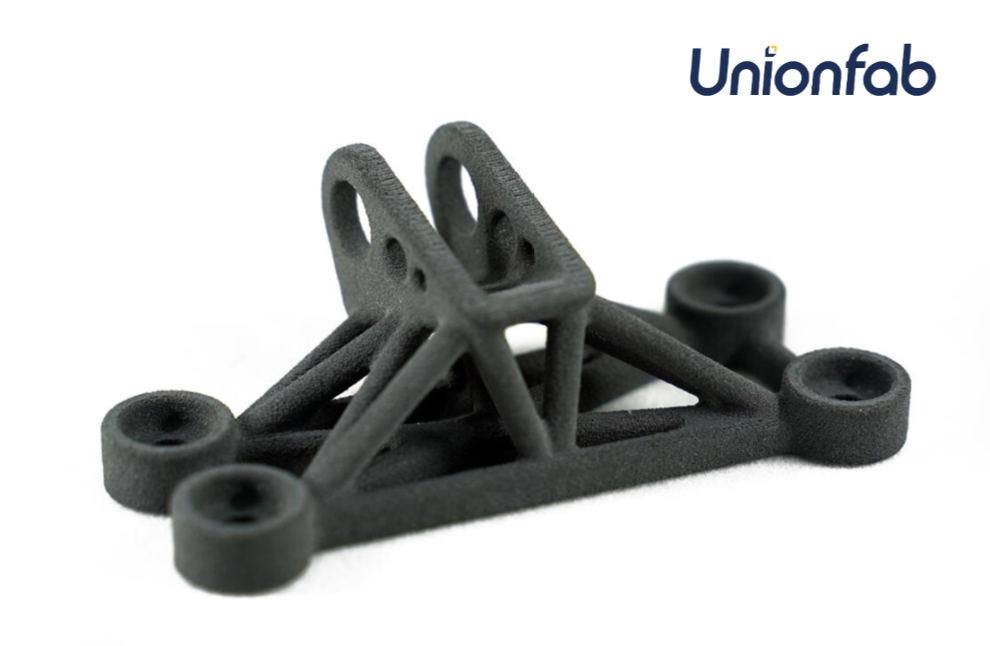

Glass-filled Nylon
Glass-filled nylon has added glass fibers to improve strength, stiffness, and heat resistance. It’s commonly used for structural parts and functional prototypes that need to withstand high stress or temperatures. However, it can be more brittle and difficult to print due to the glass fibers.
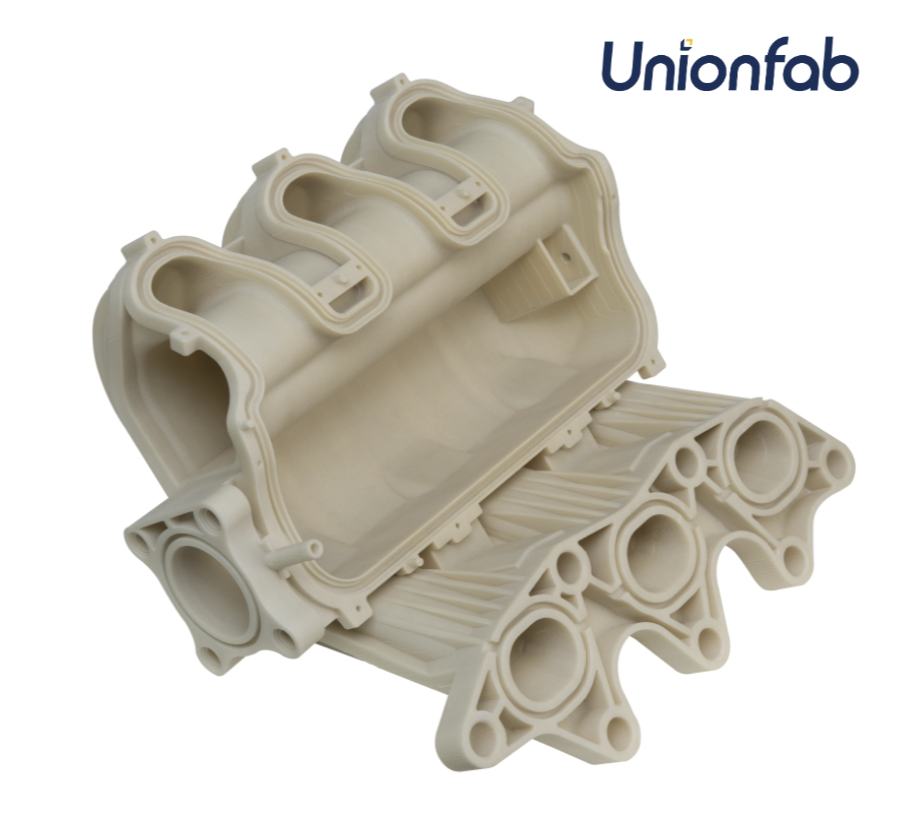

PP (Polypropylene)
Polypropylene is lightweight, resistant to chemicals, and great for parts that experience repeated movement or fatigue, like living hinges and containers. It’s used in packaging and industrial parts, though it can be tricky to print with due to its tendency to warp.

Source: asahi-kasei.co.jp
PE (Polyethylene)
Polyethylene is known for its chemical resistance, impact strength, and low friction. It’s often used for medical parts, containers, and seals. While it offers flexibility, it is less strong and rigid than some other materials like Nylon 12.

Source: rtprototype.com
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer)
TPE is a rubber-like material that combines the flexibility of elastomers with the ease of processing thermoplastics. It’s used for soft, flexible parts like grips and seals. TPE is highly impact-resistant and suitable for industries like automotive and consumer goods.
SLS Material Comparison Chart
Material | Flexibility | Strength | Chemical Resistance | Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
TPU | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | High elasticity, abrasion resistance | Automotive parts, footwear, medical devices |
Nylon 6 | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | Excellent mechanical properties, versatile | Functional prototypes, automotive, industrial |
Nylon 11 | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | High chemical resistance, low moisture absorption | Consumer goods, industrial applications |
Nylon 12 | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | High strength-to-weight ratio, smooth finish | Aerospace, automotive, functional parts |
PP | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | Excellent fatigue resistance, low cost | Packaging, automotive, medical applications |
PE | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | High chemical resistance, low moisture absorption | Consumer goods, packaging, automotive components |
TPE | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | Combines the characteristics of rubber and plastic | Grips, seals, soft-touch parts |

How to Choose the Right SLS Material
Define Your Part’s Requirements:
What level of strength or flexibility do you need?
High Strength: Nylon 12, Nylon 11, Nylon 6
High Flexibility: TPU, TPE
Balance of Strength & Flexibility: Nylon 66
Is thermal or chemical resistance a priority?
High Heat Resistance: PPSF, PEI
High Chemical Resistance: PPSF, PEI, PC
Are you focusing more on aesthetics or functionality?
Aesthetics: Nylon 11, Nylon 12 (for smoother surfaces)
Functionality: Nylon 12 (strong and versatile), Nylon 6 (cost-effective)
Match the Material to the Application:
For automotive parts, consider materials like Nylon or Glass-filled Nylon for strength and durability.
For flexible components, TPU or TPE may be ideal.
For lightweight, chemical-resistant parts, PP or PE could be the best choice.
Leverage Available Resources:
Access Material Performance Datasheets
Make informed decisions with confidence! Click to download our SLS material datasheets for a deep dive into performance metrics like strength, flexibility, and heat resistance.
Need personalized advice? Contact our experts to ensure compatibility with your design and performance needs.
Conclusion
Whether you need the flexibility of TPU, the chemical resistance of Polypropylene, or the toughness of Nylon, leveraging SLS 3D printing opens the door to versatile, efficient manufacturing solutions!
With its capacity to produce functional, end-use parts and prototypes quickly and reliably, SLS technology remains a top choice for industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to consumer goods and healthcare.


