Is Inconel Magnetic? [+Material Composition Guide]
![Is Inconel Magnetic? [+Material Composition Guide]](https://ufc-dtc-cms.oss-accelerate.aliyuncs.com/blog/20250519/173406_gt83zgqm7.png)
Learn whether Inconel is magnetic, how its composition affects magnetism, and how it performs in metal 3D printing. Includes a comparison of Inconel 625 vs 718 and real-world use cases.
Is Inconel magnetic?
In this article, we dive into the magnetic properties of Inconel and how it performs in additive manufacturing.
Whether you're engineering high-performance metal parts or sourcing materials for sensitive components, this guide will clarify Inconel’s behavior under magnetic fields—and show how Unionfab supports precision 3D printing with Inconel alloys.
You can also read our in-depth material guide on Inconel 3D printing here.
What is Inconel?
Inconel refers to a family of austenitic nickel-chromium-based superalloys developed for extreme mechanical and thermal stress. These alloys are engineered to withstand:
High temperatures (up to 1000°C and beyond)
Corrosive chemicals (e.g., saltwater, acids, oxidizers)
High-pressure environments
Inconel is commonly used in:
Turbine and jet engine components
Heat exchangers
Exhaust systems
Nuclear reactors
Rocket engine parts
Common Inconel Grades:
Inconel 625: Excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for marine and chemical applications.
Inconel 718: High strength, fatigue resistance, widely used in aerospace and automotive.
Inconel’s performance in these demanding environments has also made it a natural fit for metal 3D printing, particularly with powder bed fusion technologies.
What is Inconel Made Of?
The core elements in Inconel are nickel (Ni), chromium (Cr), and iron (Fe), along with trace additions of molybdenum, niobium, and other elements depending on the grade.
Influence on Magnetism:
Nickel: Non-magnetic in its pure form; primary reason for Inconel's overall non-magnetic behavior.
Chromium and Molybdenum: Also non-magnetic; contribute to corrosion resistance.
Iron: Can be magnetic, but its effect is reduced in austenitic matrix due to the dominance of nickel.
Composition Comparison:
Element | Inconel 625 (approx.) | Inconel 718 (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
Nickel (Ni) | ~58% | ~50–55% |
Chromium (Cr) | ~21–23% | ~17–21% |
Iron (Fe) | ~5% | Balance (~18%) |
Molybdenum (Mo) | ~8–10% | ~3% |
Niobium (Nb) | ~3–4% | ~5% |
Although both grades are austenitic and non-magnetic in the annealed state, the higher iron content in Inconel 718 can slightly increase the chance of magnetic response after cold working.
Is Inconel Magnetic?
The Short Answer:
In its standard annealed state, Inconel is non-magnetic.
Inconel alloys, especially 625 and 718, belong to the austenitic class of metals. Austenitic structures are inherently non-ferromagnetic, meaning they are not attracted to magnets under normal conditions.
However, some magnetic behavior can develop in certain situations:
Cold working or plastic deformation (e.g., machining or surface stress)
Phase transformation due to thermal or mechanical treatment
Residual stresses from rapid cooling or uneven heating
Summary Table:
Inconel Grade | Magnetic in Annealed State? | Magnetic After Cold Work? |
|---|---|---|
Inconel 625 | No | Slightly magnetic possible |
Inconel 718 | No | Slightly magnetic possible |
For most applications requiring non-magnetic performance, Inconel remains a safe and stable choice. If absolute magnetic neutrality is required (such as MRI-compatible parts), it’s recommended to verify with post-processing certification.
Why Magnetism Matters in 3D Printed Metal Parts
Magnetic properties are not just a material curiosity—they affect real-world functionality.Here’s where magnetic behavior matters:
Medical
Non-magnetic parts are essential for MRI compatibility or implants near sensitive electronics.
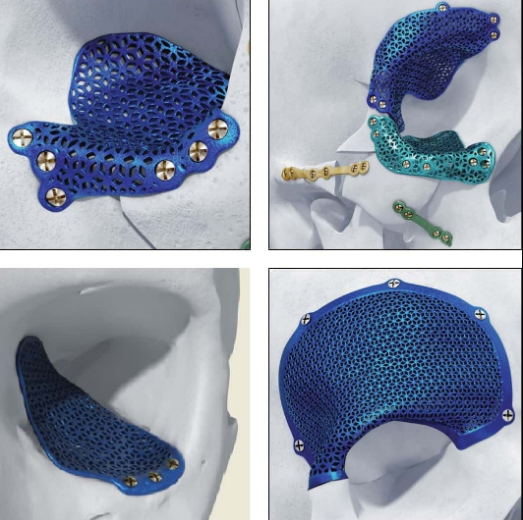
Source: jnjmedtech.com
In medical applications, non-magnetic 3D printed components are vital for MRI compatibility. Magnetic materials can interfere with imaging quality and pose safety risks. Materials like Inconel, when properly processed, offer the necessary non-magnetic properties for safe use in medical devices.
Aerospace & Defense
Avoiding interference with avionics, sensors, or communication systems.
Source: pick3dprinter.com
Electronics
Preventing unintentional electromagnetic interaction in shielding or connectors.
Source: researchgate.net
Energy
Magnetic stability is important in nuclear or turbomachinery environments.
Understanding whether Inconel is magnetic helps engineers and designers make informed choices for critical designs. With 3D printing offering the freedom to manufacture parts closer to electronic systems or sensors, the material’s magnetic behavior is even more relevant.
Can Inconel Be 3D Printed?
Yes, Inconel is highly suitable for metal additive manufacturing, especially using Selective Laser Melting (SLM) or Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS).
Key Characteristics of Inconel in 3D Printing:
High thermal strength: maintains mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
Excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance
Good fatigue and creep resistance
Suitable for complex geometries without compromising strength
Reduced need for welding or assembly (thanks to DfAM—Design for Additive Manufacturing)
Typical 3D Printed Inconel Applications:
Jet engine brackets and blades
High-temperature exhaust ducts
Heat exchangers and fluid manifolds
Custom rocket nozzle parts
Valves for chemical and marine equipmentWhile Inconel is more challenging to process than aluminum or stainless steel, experienced additive manufacturing providers like Unionfab offer the right equipment and expertise for high-quality results.
Inconel 3D Printing with Unionfab
At Unionfab, we offer end-to-end metal 3D printing services using Inconel and other advanced alloys. Our process ensures structural integrity, accuracy, and material performance that meet industry standards.
What Sets Unionfab Apart:
Industrial-grade printers: EOS, BLT, and SLM platforms
Experienced engineers: Support from design to delivery
Fast lead times: Rapid prototyping and batch production
Quality assurance: Material certification, dimensional inspection, surface checks
Get a Free Inconel 3D Printing Quote from Unionfab
Bring Your High-Performance Designs to Life
Whether you're prototyping an aerospace bracket or producing production-grade high-temp parts, Unionfab’s Inconel 3D printing service ensures precision, strength, and reliability.
Our team will help you:
Select the right grade and technology
Optimize your design for printing
Understand cost, delivery, and technical constraintsLet’s turn your designs into durable, high-performance metal components.
Contact us to get a free quote!

FAQ: Inconel & Magnetic Properties
Q: Is Inconel magnetic by nature?
A: No. Inconel is an austenitic nickel-based alloy and is non-magnetic when annealed.
Q: Can Inconel become magnetic?
A: Yes, slightly. Cold working or phase changes may cause minor magnetic properties.
Q: Is Inconel MRI-safe?
A: In general, yes. But it depends on specific processing history. Always confirm with certified test data.
Q: Can Unionfab print Inconel for aerospace or medical use?
A: Yes. We provide industrial-grade Inconel printing with material traceability and post-processing suitable for critical industries.

